Citric-acid-derived photo-cross-linked biodegradable elastomers
- PMID: 20557687
- PMCID: PMC2943534
- DOI: 10.1163/092050609X12567178204169
Citric-acid-derived photo-cross-linked biodegradable elastomers
Abstract
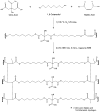
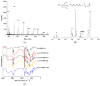
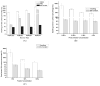
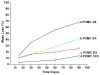
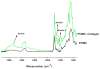
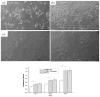
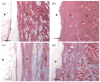
Citric-acid-derived thermally cross-linked biodegradable elastomers (CABEs) have recently received significant attention in various biomedical applications, including tissue-engineering orthopedic devices, bioimaging and implant coatings. However, citric-acid-derived photo-cross-linked biodegradable elastomers are rarely reported. Herein, we report a novel photo-cross-linked biodegradable elastomer, referred to as poly(octamethylene maleate citrate) (POMC), which preserves pendant hydroxyl and carboxylic functionalities after cross-linking for the potential conjugation of biologically active molecules. Pre-POMC is a low-molecular-mass pre-polymer with an average molecular mass between 701 and 1291 Da. POMC networks are soft and elastic with an initial modulus of 0.07 to 1.3 MPa and an elongation-at-break between 38 and 382%. FT-IR-ATR results confirmed the successful surface immobilization of type-I collagen onto POMC films, which enhanced in vitro cellular attachment and proliferation. Photo-polymerized POMC films implanted subcutaneously into Sprague-Dawley rats demonstrated minimal in vivo inflammatory responses. The development of POMC enriches the family of citric-acid-derived biodegradable elastomers and expands the available biodegradable polymers for versatile needs in biomedical applications.
Figures

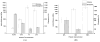
Similar articles
-
Biodegradable poly(ester urethane)urea elastomers with variable amino content for subsequent functionalization with phosphorylcholine.Acta Biomater. 2014 Nov;10(11):4639-4649. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.08.008. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Acta Biomater. 2014. PMID: 25132273 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradable nitric oxide-releasing poly(diol citrate) elastomers.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010 Apr;93(1):356-63. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.32536. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010. PMID: 19569216
-
Fluorescence imaging enabled urethane-doped citrate-based biodegradable elastomers.Biomaterials. 2013 May;34(16):4048-4056. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.02.040. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Biomaterials. 2013. PMID: 23465824 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradable elastomers for biomedical applications and regenerative medicine.Regen Med. 2014 May;9(3):385-98. doi: 10.2217/rme.14.4. Regen Med. 2014. PMID: 24935047 Review.
-
Photo-crosslinked synthetic biodegradable polymer networks for biomedical applications.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2019 Feb;30(2):77-106. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2018.1553105. Epub 2019 Jan 12. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2019. PMID: 30497347 Review.
Cited by
-
A Rheological Study of Biodegradable Injectable PEGMC/HA Composite Scaffolds.Soft Matter. 2012;8(5):1499-1507. doi: 10.1039/C1SM05786C. Soft Matter. 2012. PMID: 25309615 Free PMC article.
-
Flexible biodegradable citrate-based polymeric step-index optical fiber.Biomaterials. 2017 Oct;143:142-148. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.08.003. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Biomaterials. 2017. PMID: 28802101 Free PMC article.
-
Phototherapy and optical waveguides for the treatment of infection.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 Dec;179:114036. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.114036. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021. PMID: 34740763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Progress in Advanced Polyester Elastomers for Tissue Engineering and Bioelectronics.Molecules. 2023 Dec 9;28(24):8025. doi: 10.3390/molecules28248025. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elastomeric Polyesters in Cardiovascular Tissue Engineering and Organs-on-a-Chip.Biomacromolecules. 2023 Nov 13;24(11):4511-4531. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.3c00387. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Biomacromolecules. 2023. PMID: 37639715 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang Y, Ameer GA, Sheppard BJ, Langer R. Nature Biotechnol. 2002;20:602. - PubMed
-
- Younes HM, Bravo-Grimaldo E, Amsden BG. Biomaterials. 2004;25:5261. - PubMed
-
- Shen JY, Pan XY, Lim CH, Chan-Park MB, Zhu X, Beuerman RW. Biomacromolecules. 2007;8:376. - PubMed
-
- Huang X, Li CC, Zheng LC, Zhang D, Guan GH, Xiao YN. Polym Int. 2009;58:893.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
