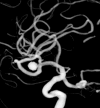
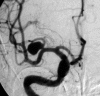
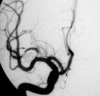
Endovascular treatment of middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Overall perioperative results. Apropos of 113 cases
- PMID: 20557720
- PMCID: PMC3396016
- DOI: 10.1177/159101990801400303
Endovascular treatment of middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Overall perioperative results. Apropos of 113 cases
Abstract
The endovascular approach is described in 113 middle cerebral artery (MCA) aneurysms. The treatment failed in six cases with no adverse clinical consequences. Out of the 107 treated cases, it was possible to obtain a complete occlusion in 50 aneurysms (47%), whereas a residual aneurysm neck was observed in 54 cases (50%). Follow-up angiograms were performed in 60 cases, showing a 22% rate of further thrombosis of the aneurysm. Recanalization of the aneurysm was observed in 8% of cases, which required retreatment. The technique-related permanent morbidity rate was 9% while the mortality rate was 2%. A review of the surgical and endovascular literature is presented. The endovascular approach is particularly indicated when normal MCA branches do not arise from the aneurysm base. It must be meticulously planned in all other cases. Endovascular coil treatment of MCA aneurysms is feasible, with acceptable morbi-mortality rates.
Figures
References
-
- Baskaya M, Coscarella E, et al. Surgical management of middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Neurosurgery Quarterly. 2005;15:201–210.
-
- Bulsara K, Tolbert M, Alexander M. Experience in the endovascular management of 76 patients with middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Annual Meeting of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons; 2006 October 7-12; Chicago (Illinois). 2006.
-
- Flamm ES, Fein JM. Middle cerebral artery aneurysms. . In: Flamm ES, Fein JM, editors. Cerebrovascular Surgery. New York: Springer-Verlag; 1985. pp. 861–877. Vol III.
-
- Hirota N, Musacchio M, et al. Angiographic and clinical results after endovascular treatment for middle cerebral artery berry aneurysms. Neuroradiology Journal. 2007;20:89–101. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources