In vivo non-linear optical (NLO) imaging in live rabbit eyes using the Heidelberg Two-Photon Laser Ophthalmoscope
- PMID: 20558159
- PMCID: PMC2922943
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2010.06.007
In vivo non-linear optical (NLO) imaging in live rabbit eyes using the Heidelberg Two-Photon Laser Ophthalmoscope
Abstract
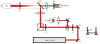
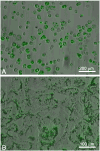
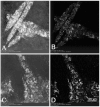
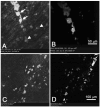
Imaging of non-linear optical (NLO) signals generated from the eye using ultrafast pulsed lasers has been limited to the study of ex vivo tissues because of the use of conventional microscopes with slow scan speeds. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of a novel, high scan rate ophthalmoscope to generate NLO signals using an attached femtosecond laser. NLO signals were generated and imaged in live, anesthetized albino rabbits using a newly designed Heidelberg Two-Photon Laser Ophthalmoscope with attached 25 mW fs laser having a central wavelength of 780 nm, pulsewidth of 75 fs, and a repetition rate of 50 MHz. To assess two-photon excited fluorescent (TPEF) signal generation, cultured rabbit corneal fibroblasts (RCF) were first labeled by Blue-green fluorescent FluoSpheres (1 mum diameter) and then cells were micro-injected into the central cornea. Clumps of RCF cells could be detected by both reflectance and TPEF imaging at 6 h after injection. By 6 days, RCF containing fluorescent microspheres confirmed by TPEF showed a more spread morphology and had migrated from the original injection site. Overall, this study demonstrates the potential of using NLO microscopy to sequentially detect TPEF signals from live, intact corneas. We conclude that further refinement of the Two-photon laser Ophthalmoscope should lead to the development of an important, new clinical instrument capable of detecting NLO signals from patient corneas.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Two-photon-excited fluorescence imaging of human RPE cells with a femtosecond Ti:Sapphire laser.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006 Oct;47(10):4553-7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-1562. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006. PMID: 17003452
-
[Two-photon microscopy of the cornea using intrinsic contrast].Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2009 Dec;226(12):970-9. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1109918. Epub 2009 Dec 15. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2009. PMID: 20108191 German.
-
Nonlinear Optical Corneal Crosslinking, Mechanical Stiffening, and Corneal Flattening Using Amplified Femtosecond Pulses.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2019 Dec 16;8(6):35. doi: 10.1167/tvst.8.6.35. eCollection 2019 Nov. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2019. PMID: 31890347 Free PMC article.
-
Femtosecond Lasers in Cornea & Refractive Surgery.Exp Eye Res. 2021 Apr;205:108477. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108477. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Exp Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 33516763 Review.
-
Two-Photon Imaging for Non-Invasive Corneal Examination.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 11;22(24):9699. doi: 10.3390/s22249699. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36560071 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo two-photon microscopy of the human eye.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 12;9(1):10121. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46568-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31300680 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo structural imaging of the cornea by polarization-resolved second harmonic microscopy.Biomed Opt Express. 2012 Jan 1;3(1):1-15. doi: 10.1364/BOE.3.000001. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2012. PMID: 22254163 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution, noninvasive, two-photon fluorescence measurement of molecular concentrations in corneal tissue.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Apr 20;52(5):2556-64. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-6620. Print 2011 Apr. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21228379 Free PMC article.
-
Femtosecond infrared intrastromal ablation and backscattering-mode adaptive-optics multiphoton microscopy in chicken corneas.Biomed Opt Express. 2011 Nov 1;2(11):2950-60. doi: 10.1364/BOE.2.002950. Epub 2011 Oct 3. Biomed Opt Express. 2011. PMID: 22076258 Free PMC article.
-
Blind deconvolution of second harmonic microscopy images of the living human eye.Biomed Opt Express. 2023 Apr 19;14(5):2117-2128. doi: 10.1364/BOE.486989. eCollection 2023 May 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2023. PMID: 37206134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cavanagh HD, Petroll WM, Alizadeh H, He YG, McCulley JP, Jester JV. Clinical and diagnostic use of in vivo confocal microscopy in patients with corneal disease. Ophthalmology. 1993;100:1444–1454. - PubMed
-
- Chang JH, Ren HW, Petroll MW, Cavanagh DH, Jester JV. The application of in vivo confocal microscopy and tear LDH measurement in assessing corneal response to contact lens and contact lens solutions. Curr Eye Res. 1999;19:171–181. - PubMed
-
- Chen SY, Yu HC, Wang IJ, Sun CK. Infrared-based third and second harmonic generation imaging of cornea. J Biomed Opt. 2009;14:044012. - PubMed
-
- Denk W, Strickler JH, Webb WW. Two-photon laser scanning fluorescence microscopy. Science. 1990;248:73–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

