Prolonged depletion of circulating CD4+ T lymphocytes and acute monocytosis after pantropic canine coronavirus infection in dogs
- PMID: 20558216
- PMCID: PMC7114409
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.06.006
Prolonged depletion of circulating CD4+ T lymphocytes and acute monocytosis after pantropic canine coronavirus infection in dogs
Abstract
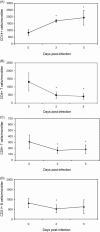
A hypervirulent strain (CB/05) of canine coronavirus was employed to infect oronasally 11-week-old pups. Peripheral blood monocytes (CD14(+)), T lymphocytes (CD4(+) and CD8(+)) and B lymphocytes (CD21(+)) were studied by flow cytometry within 5 days post-infection (p.i.) and at later time points. Infection with CB/05 resulted in a profound depletion of T cells and a slight loss of B cells in the first week p.i. In particular, while the CD8(+) and the B lymphocytes returned to baseline levels by day 7 p.i., the CD4(+) T cells remained significantly low until day 30 p.i. and recovered completely only at day 60 p.i. Monocytosis was also observed after CB/05 infection with a peak at day 5 p.i. The prolonged depletion of peripheral CD4(+) T cells did not alter the levels of serum IgG or IgM. The impact of CB/05 infection on the immune performance of infected pups is discussed.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Auwaerter P.G., Rota P.A., Elkins W.R., Adams R.J., DeLozier T., Shi Y., Bellini W.J., Murphy B.R., Griffin D.E. Measles virus infection in rhesus macaques: altered immune responses and comparison of the virulence of six different virus strains. J. Infect. Dis. 1999;180:950–958. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

