Chronic disease modeling and simulation software
- PMID: 20558320
- PMCID: PMC2934868
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbi.2010.06.003
Chronic disease modeling and simulation software
Abstract
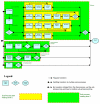
Computers allow describing the progress of a disease using computerized models. These models allow aggregating expert and clinical information to allow researchers and decision makers to forecast disease progression. To make this forecast reliable, good models and therefore good modeling tools are required. This paper will describe a new computer tool designed for chronic disease modeling. The modeling capabilities of this tool were used to model the Michigan model for diabetes. The modeling approach and its advantages such as simplicity, availability, and transparency are discussed.
Figures


References
-
- Brennan A, Chick SE, Davies R. A taxonomy of model structures for economic evaluation of health technologies. Health Econ. 2006;15:1295–1310. DOI:10.1002/hec.1148. - PubMed
-
- Weinstein MC, O'Brien B, Hornberger J, Jackson J, Johannesson M, McCabe C, Luce BR. Principles of good practice for decision analytic modeling in health-care evaluation: report of the ISPOR Task Force on Good Research Practices–Modeling Studies. Value Health. 6:9–17. - PubMed
- American Diabetes Association Consensus Panel Guidelines for computer modeling of diabetes and its complications (Consensus Statement) Diabetes Care. 2004;27:2262–2265. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association Consensus Panel Guidelines for computer modeling of diabetes and its complications (Consensus Statement) Diabetes Care. 2004;27:2262–2265. - PubMed
-
- The Mount Hood 4 Modeling Group Computer modeling of diabetes and its complications: a report on the Fourth Mount Hood Challenge Meeting. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:1638–1646. doi: 10.2337/dc07-9919. - PubMed
-
- Eddy DM, Schlessinger L. Archimedes: a trial-validated model of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003 Nov;26(11):3093–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

