Relationship between inpatient hyperglycemia and insulin treatment after kidney transplantation and future new onset diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 20558559
- PMCID: PMC2974410
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.09481209
Relationship between inpatient hyperglycemia and insulin treatment after kidney transplantation and future new onset diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background and objectives: Approximately two-thirds of kidney transplant recipients with no previous history of diabetes experience inpatient hyperglycemia immediately after kidney transplant surgery; whether inpatient hyperglycemia predicts future new onset diabetes after transplant (NODAT) is not established.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: A retrospective study was conducted to determine the risk conferred by inpatient hyperglycemia on development of NODAT within 1 year posttransplant. All adult nondiabetic kidney transplant recipients between June 1999 and January 2008 were included. Posttransplant inpatient hyperglycemia was defined as any bedside capillary blood glucose > or = 200 mg/dl or insulin therapy during hospitalization. NODAT was defined as HbA1C > or = 6.5%, fasting venous serum glucose > or = 126 mg/dl, or prescribed diet or medical therapy for diabetes mellitus.
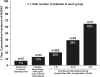
Results: The study cohort included 377 patients. NODAT developed in 1 (4%) of the 28 patients without inpatient hyperglycemia, 4 (18%) of the 22 patients with inpatient hyperglycemia but not treated with insulin, and in 98 (30%) of the 327 of the patients who were diagnosed with inpatient hyperglycemia and were treated with insulin. In adjusted analyses, requirement of insulin therapy during hospitalization posttransplant was associated with a 4-fold increase in NODAT (relative risk 4.01; confidence interval, 1.49 to 10.7; P = 0.006).
Conclusion: Development of inpatient hyperglycemia after kidney transplantation in nondiabetic patients significantly increased the risk of NODAT. Additionally, we observed a significantly increased risk of cardiovascular events in patients who developed NODAT.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early Postoperative Basal Insulin Therapy versus Standard of Care for the Prevention of Diabetes Mellitus after Kidney Transplantation: A Multicenter Randomized Trial.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Aug;32(8):2083-2098. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2021010127. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34330770 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hyperglycemia during the immediate period after kidney transplantation.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 Apr;4(4):853-9. doi: 10.2215/CJN.05471008. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19339426 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, prospective trial to evaluate the effect of vildagliptin in new-onset diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation.Trials. 2010 Oct 6;11:91. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-11-91. Trials. 2010. PMID: 20925938 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prevention and management of new-onset diabetes mellitus in kidney transplantation.Neth J Med. 2014 Apr;72(3):127-34. Neth J Med. 2014. PMID: 24846925 Review.
-
Diagnosis, management and treatment of glucometabolic disorders emerging after kidney transplantation: a position statement from the Nordic Transplantation Societies.Transpl Int. 2013 Nov;26(11):1049-60. doi: 10.1111/tri.12112. Epub 2013 May 2. Transpl Int. 2013. PMID: 23634804 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-transplant diabetes mellitus: risk factors and outcomes in a 5-year follow-up.Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2024 Jan 30;5:1336896. doi: 10.3389/fcdhc.2024.1336896. eCollection 2024. Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2024. PMID: 38352660 Free PMC article.
-
New-onset diabetes after kidney transplant in children.Pediatr Nephrol. 2015 Mar;30(3):405-16. doi: 10.1007/s00467-014-2830-7. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Pediatr Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 24894384 Review.
-
Hyperglycemia during the immediate period following liver transplantation.Future Sci OA. 2016 Jan 27;2(1):FSO97. doi: 10.4155/fsoa-2015-0010. eCollection 2016 Mar. Future Sci OA. 2016. PMID: 28031946 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized controlled trial-based algorithm for insulin-pump therapy in hyperglycemic patients early after kidney transplantation.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 8;13(3):e0193569. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193569. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29518094 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term Management of the Adult Liver Transplantation Recipients.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2021 Mar-Apr;11(2):239-253. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2020.06.010. Epub 2020 Jul 2. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33746450 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cosio FG, Pesavento TE, Kim S, Osei K, Henry M, Ferguson RM: Patient survival after renal transplantation: IV. Impact of post-transplant diabetes. Kidney Int 62: 1440–1446, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Kasiske BL, Snyder JJ, Gilbertson D, Matas AJ: Diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation in the United States. Am J Transplant 3: 178–185, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Nam JH, Mun JI, Kim SI, Kang SW, Choi KH, Park K, Ahn CW, Cha BS, Song YD, Lim SK, Kim KR, Lee HC, Huh KB: Beta-Cell dysfunction rather than insulin resistance is the main contributing factor for the development of postrenal transplantation diabetes mellitus. Transplantation 71: 1417–1423, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Woodward RS, Schnitzler MA, Baty J, Lowell JA, Lopez-Rocafort L, Haider S, Woodworth TG, Brennan DC: Incidence and cost of new onset diabetes mellitus among U.S. wait-listed and transplanted renal allograft recipients. Am J Transplant 3: 590–598, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Ducloux D, Kazory A, Chalopin JM: Posttransplant diabetes mellitus and atherosclerotic events in renal transplant recipients: A prospective study. Transplantation 79: 438–443, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical