Mesenchymal stem cells, used as bait, disclose tissue binding sites: a tool in the search for the niche?
- PMID: 20558574
- PMCID: PMC2913365
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090984
Mesenchymal stem cells, used as bait, disclose tissue binding sites: a tool in the search for the niche?
Abstract
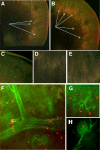
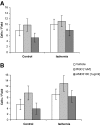
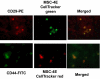
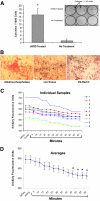
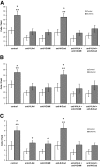
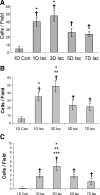
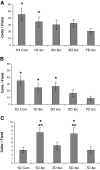
We developed an ex vivo approach characterizing renal mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) adhesion to kidney sections. Specificity of MSC adhesion was confirmed by demonstrating a) 3T3 cells displayed 10-fold lower adhesion, and b) MSC adhesion was CXCR4/stromal-derived factor-1 (SDF-1)-dependent. MSC adhesion was asymmetrical, with postischemic sections exhibiting more than twofold higher adhesion than controls, and showed preference to perivascular areas. Pretreating kidney sections with cyclic arginine-glycine-aspartic acid peptide resulted in increased MSC adhesion (by displacing resident cells), whereas blockade of CXCR4 with AMD3100 and inhibition of alpha4beta1(VLA4) integrin or vascular cellular adhesion molecule-1, reduced adhesion. The difference between adhered cells under cyclic arginine-glycine-aspartic acid peptide-treated and control conditions reflected prior occupancy of binding sites with endogenous cells. The AMD3100-inhibitable fraction of adhesion reflected CXCR4-dependent adhesion, whereas maximal adhesion was interpreted as kidney MSC-lodging capacity. MSC obtained from mice overexpressing caveolin-1 exhibited more robust adhesion than those obtained from knockout animals, consistent with CXCR4 dimerization in caveolae. These data demonstrate a) CXCR4/SDF-1-dependent adhesion increases in ischemia; b) CXCR4/SDF-1 activation is dependent on MSC surface caveolin-1; and c) occupancy of MSC binding sites is decreased, while d) capacity of MSC binding sites is expanded in postischemic kidneys. In conclusion, we developed a cell-bait strategy to unmask renal stem cell binding sites, which may potentially shed light on the MSC niche(s) and its characteristics.
Figures
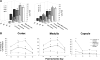


Similar articles
-
Postobstructive regeneration of kidney is derailed when surge in renal stem cells during course of unilateral ureteral obstruction is halted.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):F357-64. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00542.2009. Epub 2009 Nov 11. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19906947 Free PMC article.
-
VEGF/SDF-1 promotes cardiac stem cell mobilization and myocardial repair in the infarcted heart.Cardiovasc Res. 2011 Aug 1;91(3):402-11. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr053. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21345805 Free PMC article.
-
Role of SDF-1:CXCR4 in Impaired Post-Myocardial Infarction Cardiac Repair in Diabetes.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018 Jan;7(1):115-124. doi: 10.1002/sctm.17-0172. Epub 2017 Nov 9. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29119710 Free PMC article.
-
SDF-1 secreted by mesenchymal stem cells promotes the migration of endothelial progenitor cells via CXCR4/PI3K/AKT pathway.J Mol Histol. 2021 Dec;52(6):1155-1164. doi: 10.1007/s10735-021-10008-y. Epub 2021 Oct 12. J Mol Histol. 2021. PMID: 34642827
-
The surface adhesion molecule CXCR4 stimulates mesenchymal stem cell migration to stromal cell-derived factor-1 in vitro but does not decrease apoptosis under serum deprivation.Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2006 Jan-Mar;7(1):19-24. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2005.10.008. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2006. PMID: 16513519
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal stem cells promote mammary cancer cell migration in vitro via the CXCR2 receptor.Cancer Lett. 2011 Sep 1;308(1):91-9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.04.018. Epub 2011 May 23. Cancer Lett. 2011. PMID: 21601983 Free PMC article.
-
Paracrine molecules of mesenchymal stem cells for hematopoietic stem cell niche.Bone Marrow Res. 2011;2011:353878. doi: 10.1155/2011/353878. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Bone Marrow Res. 2011. PMID: 22046560 Free PMC article.
-
Concise review: different mesenchymal stromal/stem cell populations reside in the adult kidney.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014 Dec;3(12):1451-5. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2014-0142. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 25355731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The less-often-traveled surface of stem cells: caveolin-1 and caveolae in stem cells, tissue repair and regeneration.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013 Jul 30;4(4):90. doi: 10.1186/scrt276. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 23899671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caveolin-1: A Review of Intracellular Functions, Tissue-Specific Roles, and Epithelial Tight Junction Regulation.Biology (Basel). 2023 Nov 5;12(11):1402. doi: 10.3390/biology12111402. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998001 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schofield R. The relationship between the spleen colony-forming cell and the hematopoietic stem cell. Blood Cells. 1978;4:7–25. - PubMed
-
- Moore K, Lemischka I. Stem cells and their niches. Science. 2006;311:1880–1885. - PubMed
-
- Xie T, L Li. Stem cells and their niche: an inseparable relationship. Development. 2007;134:2001–2006. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Niu C, Ye L, Huang H, He X, Tong W, Ross J, Haug J, Johnson T, Feng J, Harris S, Wiedemann L, Mishina Y, Li L. Identification of the haematopoietic stem cell niche and control of the niche size. Nature. 2003;425:836–841. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

