Long-term expression of tissue-inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in the murine central nervous system does not alter the morphological and behavioral phenotype but alleviates the course of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 20558576
- PMCID: PMC2913353
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090918
Long-term expression of tissue-inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in the murine central nervous system does not alter the morphological and behavioral phenotype but alleviates the course of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis
Abstract
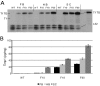
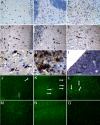
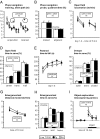
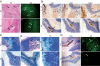
Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) are a family of closely related proteins that inhibit matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). In the central nervous system (CNS), TIMPs 2, 3, and 4 are constitutively expressed at high levels, whereas TIMP1 can be induced by various stimuli. Here, we studied the effects of constitutive expression of TIMP1 in the CNS in transgenic mice. Transgene expression started prenatally and persisted throughout lifetime at high levels. Since MMP activity has been implicated in CNS development, in proper function of the adult CNS, and in inflammatory disorders, we investigated Timp1-induced CNS alterations. Despite sufficient MMP inhibition, high expressor transgenic mice had a normal phenotype. The absence of compensatory up-regulation of MMP genes in the CNS of Timp1 transgenic mice indicates that development, learning, and memory functions do not require the entire MMP arsenal. To elucidate the effects of strong Timp1 expression in CNS inflammation, we induced experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. We observed a Timp1 dose-dependent mitigation of both experimental allergic encephalomyelitis symptoms and histological lesions in the CNS of transgenic mice. All in all, our data demonstrate that (1) long-term CNS expression of TIMP1 with complete suppression of gelatinolytic activity does not interfere with physiological brain function and (2) TIMP1 might constitute a promising candidate for long-term therapeutic treatment of inflammatory CNS diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Coordinated induction of extracellular proteolysis systems during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice.Am J Pathol. 2001 Dec;159(6):2227-37. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63073-8. Am J Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11733372 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of natalizumab treatment on metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020 Apr;71(2). doi: 10.26402/jpp.2020.2.11. Epub 2020 Aug 8. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32776909
-
Differential expression of matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase genes in the mouse central nervous system in normal and inflammatory states.Am J Pathol. 1998 Mar;152(3):729-41. Am J Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9502415 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1: the TIMPed balance of matrix metalloproteinases in the central nervous system.J Neurosci Res. 2003 Dec 15;74(6):801-6. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10835. J Neurosci Res. 2003. PMID: 14648584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The TIMPs tango with MMPs and more in the central nervous system.J Neurosci Res. 2004 Jan 1;75(1):1-11. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10836. J Neurosci Res. 2004. PMID: 14689443 Review.
Cited by
-
MMP-independent role of TIMP-1 at the blood brain barrier during viral encephalomyelitis.ASN Neuro. 2013 Nov 26;5(5):e00127. doi: 10.1042/AN20130033. ASN Neuro. 2013. PMID: 24156369 Free PMC article.
-
Akt and c-Myc induce stem-cell markers in mature primary p53⁻/⁻ astrocytes and render these cells gliomagenic in the brain of immunocompetent mice.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56691. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056691. Epub 2013 Feb 12. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23424671 Free PMC article.
-
A dual role for microglia in promoting tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP) expression in glial cells in response to neuroinflammatory stimuli.J Neuroinflammation. 2011 Jun 1;8:61. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-61. J Neuroinflammation. 2011. PMID: 21631912 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinases, synaptic injury, and multiple sclerosis.Front Psychiatry. 2010 Oct 5;1:130. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2010.00130. eCollection 2010. Front Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 21423441 Free PMC article.
-
Friends or Foes: Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Multifaceted Roles in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:620581. doi: 10.1155/2015/620581. Epub 2015 Oct 11. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 26538832 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leco K, Hayden L, Sharma R, Rocheleau H, Greenberg A, Edwards D. Differential regulation of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 mRNA expression in normal and Ha-ras-transformed murine fibroblasts. Gene. 1992;117:209–217. - PubMed
-
- Ulrich R, Gerhauser I, Seeliger F, Baumgärtner W, Alldinger S. Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in the developing mouse brain and spinal cord: a reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction study. Dev Neurosci. 2005;27:408–418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

