Delineation of the Xrcc4-interacting region in the globular head domain of cernunnos/XLF
- PMID: 20558749
- PMCID: PMC2924081
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.138156
Delineation of the Xrcc4-interacting region in the globular head domain of cernunnos/XLF
Abstract
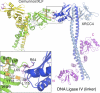
In mammals, the majority of DNA double-strand breaks are processed by the nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathway, composed of seven factors: Ku70, Ku80, DNA-PKcs, Artemis, Xrcc4 (X4), DNA-ligase IV (L4), and Cernunnos/XLF. Cernunnos is part of the ligation complex, constituted by X4 and L4. To improve our knowledge on the structure and function of Cernunnos, we performed a systematic mutagenesis study on positions selected from an analysis of the recent three-dimensional structures of this factor. Ten of 27 screened mutants were nonfunctional in several DNA repair assays. Outside amino acids critical for the expression and stability of Cernunnos, we identified three amino acids (Arg(64), Leu(65), and Leu(115)) essential for the interaction with X4 and the proper function of Cernunnos. Docking the crystal structures of the two factors further validated this probable interaction surface of Cernunnos with X4.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Structural characterization of filaments formed by human Xrcc4-Cernunnos/XLF complex involved in nonhomologous DNA end-joining.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Aug 2;108(31):12663-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1100758108. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21768349 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal domain of Cernunnos/XLF is dispensable for DNA repair in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Mar;29(5):1116-22. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01521-08. Epub 2008 Dec 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19103754 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Cernunnos-XLF and nonhomologous end-joining proteins at DNA ends in the cell.J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 2;282(44):31937-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704554200. Epub 2007 Aug 24. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17720816
-
Cernunnos/XLF: a new player in DNA double-strand break repair.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Jun;41(6):1237-40. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.10.005. Epub 2008 Oct 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 18992362 Review.
-
XLF/Cernunnos: An important but puzzling participant in the nonhomologous end joining DNA repair pathway.DNA Repair (Amst). 2017 Oct;58:29-37. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.08.003. Epub 2017 Aug 18. DNA Repair (Amst). 2017. PMID: 28846869 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural characterization of filaments formed by human Xrcc4-Cernunnos/XLF complex involved in nonhomologous DNA end-joining.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Aug 2;108(31):12663-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1100758108. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21768349 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of DNA damage, repair, and mutagenesis.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2017 Jun;58(5):235-263. doi: 10.1002/em.22087. Epub 2017 May 9. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2017. PMID: 28485537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two distinct long-range synaptic complexes promote different aspects of end processing prior to repair of DNA breaks by non-homologous end joining.Mol Cell. 2023 Mar 2;83(5):698-714.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.01.012. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Mol Cell. 2023. PMID: 36724784 Free PMC article.
-
A single XLF dimer bridges DNA ends during nonhomologous end joining.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2018 Sep;25(9):877-884. doi: 10.1038/s41594-018-0120-y. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30177755 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational phospho-mimicry reveals a regulatory role for the XRCC4 and XLF C-terminal tails in modulating DNA bridging during classical non-homologous end joining.Elife. 2017 May 13;6:e22900. doi: 10.7554/eLife.22900. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28500754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahnesorg P., Smith P., Jackson S. P. (2006) Cell 124, 301–313 - PubMed
-
- Buck D., Malivert L., de Chasseval R., Barraud A., Fondanèche M. C., Sanal O., Plebani A., Stéphan J. L., Hufnagel M., le Deist F., Fischer A., Durandy A., de Villartay J. P., Revy P. (2006) Cell 124, 287–299 - PubMed
-
- Callebaut I., Malivert L., Fischer A., Mornon J. P., Revy P., de Villartay J. P. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281, 13857–13860 - PubMed
-
- Moshous D., Callebaut I., de Chasseval R., Corneo B., Cavazzana-Calvo M., Le Deist F., Tezcan I., Sanal O., Bertrand Y., Philippe N., Fischer A., de Villartay J. P. (2001) Cell 105, 177–186 - PubMed
-
- de Villartay J. P., Fischer A., Durandy A. (2003) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3, 962–972 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

