Membrane blebbing as an assessment of functional rescue of dysferlin-deficient human myotubes via nonsense suppression
- PMID: 20558759
- PMCID: PMC3774516
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01366.2009
Membrane blebbing as an assessment of functional rescue of dysferlin-deficient human myotubes via nonsense suppression
Abstract
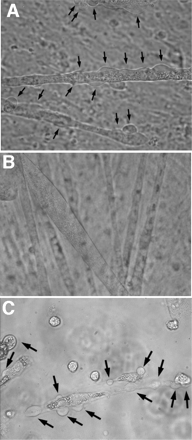
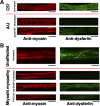
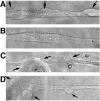
Mutations that result in the loss of the protein dysferlin result in defective muscle membrane repair and cause either a form of limb girdle muscular dystrophy (type 2B) or Miyoshi myopathy. Most patients are compound heterozygotes, often carrying one allele with a nonsense mutation. Using dysferlin-deficient mouse and human myocytes, we demonstrated that membrane blebbing in skeletal muscle myotubes in response to hypotonic shock requires dysferlin. Based on this, we developed an in vitro assay to assess rescue of dysferlin function in skeletal muscle myotubes. This blebbing assay may be useful for drug discovery/validation for dysferlin deficiency. With this assay, we demonstrate that the nonsense suppression drug, ataluren (PTC124), is able to induce read-through of the premature stop codon in a patient with a R1905X mutation in dysferlin and produce sufficient functional dysferlin (approximately 15% of normal levels) to rescue myotube membrane blebbing. Thus ataluren is a potential therapeutic for dysferlin-deficient patients harboring nonsense mutations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Defective membrane repair in dysferlin-deficient muscular dystrophy.Nature. 2003 May 8;423(6936):168-72. doi: 10.1038/nature01573. Nature. 2003. PMID: 12736685
-
Genetic manipulation of dysferlin expression in skeletal muscle: novel insights into muscular dystrophy.Am J Pathol. 2009 Nov;175(5):1817-23. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.090107. Epub 2009 Oct 15. Am J Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19834057 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasomal inhibition restores biological function of mis-sense mutated dysferlin in patient-derived muscle cells.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 23;287(13):10344-10354. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.329078. Epub 2012 Feb 8. J Biol Chem. 2012. Retraction in: J Biol Chem. 2017 Jul 28;292(30):12542. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A111.329078. PMID: 22318734 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Dysferlin and the plasma membrane repair in muscular dystrophy.Trends Cell Biol. 2004 Apr;14(4):206-13. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2004.03.001. Trends Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15066638 Review.
-
Dysferlin and muscular dystrophy.Acta Neurol Belg. 2000 Sep;100(3):142-5. Acta Neurol Belg. 2000. PMID: 11098285 Review.
Cited by
-
AMPK Complex Activation Promotes Sarcolemmal Repair in Dysferlinopathy.Mol Ther. 2020 Apr 8;28(4):1133-1153. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.02.006. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Mol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32087766 Free PMC article.
-
Exon 32 Skipping of Dysferlin Rescues Membrane Repair in Patients' Cells.J Neuromuscul Dis. 2015 Sep 2;2(3):281-290. doi: 10.3233/JND-150109. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2015. PMID: 27858744 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of nonsense mutations as a therapeutic approach to treat genetic diseases.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Nov-Dec;2(6):837-52. doi: 10.1002/wrna.95. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21976286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translational research and therapeutic perspectives in dysferlinopathies.Mol Med. 2011 Sep-Oct;17(9-10):875-82. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00084. Epub 2011 May 6. Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21556485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aminoglycosides, but not PTC124 (Ataluren), rescue nonsense mutations in the leptin receptor and in luciferase reporter genes.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 21;7(1):1020. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01093-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28432296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bansal D, Campbell KP. Dysferlin and the plasma membrane repair in muscular dystrophy. Trends Cell Biol 14: 206–213, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Bansal D, Miyake K, Vogel SS, Groh S, Chen CC, Williamson R, McNeil PL, Campbell KP. Defective membrane repair in dysferlin-deficient muscular dystrophy. Nature 423: 168–172, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Bashir R, Britton S, Strachan T, Keers S, Vafiadaki E, Lako M, Richard I, Marchand S, Bourg N, Argov Z, Sadeh M, Mahjneh I, Marconi G, Passos-Bueno MR, Moreira Ede S, Zatz M, Beckmann JS, Bushby K. A gene related to Caenorhabditis elegans spermatogenesis factor fer-1 is mutated in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2B. Nat Genet 20: 37–42, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Bittner RE, Anderson LV, Burkhardt E, Bashir R, Vafiadaki E, Ivanova S, Raffelsberger T, Maerk I, Höger H, Jung M, Karbasiyan M, Storch M, Lassmann H, Moss JA, Davison K, Harrison R, Bushby KM, Reis A. Dysferlin deletion in SJL mice (SJL-Dysf) defines a natural model for limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2B. Nat Genet 23: 141–142, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

