Role of protein transamidation in serotonin-induced proliferation and migration of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 20558776
- PMCID: PMC3095926
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0078OC
Role of protein transamidation in serotonin-induced proliferation and migration of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells
Abstract
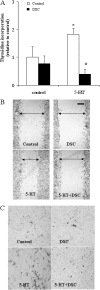
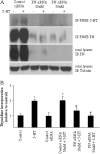
Pulmonary hypertension is characterized by elevated pulmonary artery pressure and pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell (SMC) proliferation and migration. Clinical and experimental evidence suggests that serotonin (5-HT) is important in these responses. We previously demonstrated the participation of the 5-HT transporter and intracellular 5-HT (5-HTi) in the pulmonary vascular SMC-proliferative response to 5-HT. However, the mechanism underlying the intracellular actions of 5-HT is unknown. We speculated that 5-HTi activates SMC growth by post-translational transamidation of proteins via transglutaminase (TGase) activity, a process referred to as serotonylation. To test this hypothesis, serotonylation of pulmonary artery SMC proteins, and their role in 5-HT-induced proliferative and migratory responses, were assessed. 5-HT caused dose- and time-dependent increase in serotonylation of multiple proteins in both bovine and rat pulmonary artery SMCs. Inhibition of TGase with dansylcadaverin blocked this activity, as well as SMC-proliferative and migratory responses to 5-HT. Serotonylation of proteins also was blocked by 5-HT transporter inhibitors, and was enhanced by inhibition of monoamine oxidase, an enzyme known to degrade 5-HTi, indicating that 5-HTi levels regulate serotonylation. Immunoprecipitation assays and HPLC-mass spectral peptide sequencing revealed that a major protein serotonylated by TGase was fibronectin (FN). 5-HT-stimulated SMC serotonylation and proliferation were blocked by FN small interfering (si) RNA. These findings, together with previous observations that FN expression in the lung strongly correlates with the progression of pulmonary hypertension in both experimental animals and humans, suggest an important role of FN serotonylation in the pathogenesis of this disease.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tissue transglutaminase promotes serotonin-induced AKT signaling and mitogenesis in pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells.Cell Signal. 2014 Dec;26(12):2818-25. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.09.002. Epub 2014 Sep 15. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 25218191 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonylated fibronectin is elevated in pulmonary hypertension.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 Jun 15;302(12):L1273-9. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00082.2012. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22523280 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase D signaling in serotonin-induced mitogenesis of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008 Sep;295(3):L471-8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00071.2008. Epub 2008 Jul 11. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18621911 Free PMC article.
-
Transglutaminase 2-mediated serotonylation in pulmonary hypertension.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014 Feb 15;306(4):L309-15. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00321.2013. Epub 2013 Dec 27. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24375797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonylation and Transamidation of Other Monoamines.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Jul 15;6(7):961-9. doi: 10.1021/cn500329r. Epub 2015 Feb 5. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25615632 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Serotonylation and SERT Posttranslational Modifications in Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis.Aging Dis. 2024 Mar 28;16(2):841-858. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.0328. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 39254383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor use is associated with right ventricular structure and function: the MESA-right ventricle study.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30480. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030480. Epub 2012 Feb 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22363441 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of Transglutaminase-Mediated Protein Serotonylation in the Epigenetic Landscape, Small Cell Lung Cancer, and Beyond.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 20;15(4):1332. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041332. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of allergic lung inflammation by endothelial cell transglutaminase 2.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015 Sep 15;309(6):L573-83. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00199.2015. Epub 2015 Jul 24. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26209276 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin potentiates transforming growth factor-beta3 induced biomechanical remodeling in avian embryonic atrioventricular valves.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42527. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042527. Epub 2012 Aug 6. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22880017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rudolph AM, Paul MH. Pulmonary and systemic vascular response to continuous infusion of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) in the dog. Am J Physiol 1957;189:263–268. - PubMed
-
- Lee SL, Simon AR, Wang WW, Fanburg BLH. (2)O(2) signals 5-HT–induced ERK MAP kinase activation and mitogenesis of smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol 2001;281:L646–L652. - PubMed
-
- Lee SL, Wang WW, Lanzillo JJ, Fanburg BL. Regulation of serotonin-induced DNA synthesis of bovine pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol 1994;266:L53–L60. - PubMed
-
- Coatrieux C, Sanson M, Negre-Salvayre A, Parini A, Hannun Y, Itohara S, Salvayre R, Auge N. MAO-A–induced mitogenic signaling is mediated by reactive oxygen species, MMP-2, and the sphingolipid pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 2007;43:80–89. - PubMed
-
- Eddahibi S, Guignabert C, Barlier-Mur AM, Dewachter L, Fadel E, Dartevelle P, Humbert M, Simonneau G, Hanoun N, Saurini F, et al. Cross talk between endothelial and smooth muscle cells in pulmonary hypertension: critical role for serotonin-induced smooth muscle hyperplasia. Circulation 2006;113:1857–1864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

