Weight loss with naltrexone SR/bupropion SR combination therapy as an adjunct to behavior modification: the COR-BMOD trial
- PMID: 20559296
- PMCID: PMC4459776
- DOI: 10.1038/oby.2010.147
Weight loss with naltrexone SR/bupropion SR combination therapy as an adjunct to behavior modification: the COR-BMOD trial
Abstract
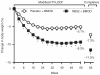
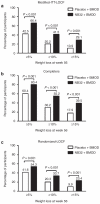
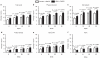
This 56-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial examined the efficacy and safety of naltrexone plus bupropion as an adjunct to intensive behavior modification (BMOD). A total of 793 participants (BMI = 36.5 ± 4.2 kg/m²) was randomly assigned in a 1:3 ratio to: (i) placebo + BMOD (N = 202); or (ii) naltrexone sustained-release (SR, 32 mg/day), combined with bupropion SR (360 mg/day) plus BMOD (i.e., NB32 + BMOD; N = 591). Both groups were prescribed an energy-reduced diet and 28 group BMOD sessions. Co-primary end points were percentage change in weight and the proportion of participants who lost ≥5% weight at week 56. Efficacy analyses were performed on a modified intent-to-treat population (ITT; i.e., participants with ≥1 postbaseline weight while taking study drug (placebo + BMOD, N = 193; NB32 + BMOD, N = 482)). Missing data were replaced with the last observation obtained on study drug. At week 56, weight loss was 5.1 ± 0.6% with placebo + BMOD vs. 9.3 ± 0.4% with NB32 + BMOD (P < 0.001). A completers analysis revealed weight losses of 7.3 ± 0.9% (N = 106) vs. 11.5 ± 0.6% (N = 301), respectively (P < 0.001). A third analysis, which included all randomized participants, yielded losses of 4.9 ± 0.6 vs. 7.8 ± 0.4%, respectively (P < 0.001). Significantly more NB32 + BMOD- vs. placebo + BMOD-treated participants lost ≥5 and ≥10% of initial weight, and the former had significantly greater improvements in markers of cardiometabolic disease risk. NB32 + BMOD was generally well tolerated, although associated with more reports of nausea than placebo + BMOD. The present findings support the efficacy of combined naltrexone/bupropion therapy as an adjunct to intensive BMOD for obesity.
Figures
References
-
- Naltrexone hydrochloride (naltrexone hydrochloride) [package insert] Barr Laboratories; Pomona, NY: 2003.
-
- Berg BJ, Pettinati HM, Volpicelli JR. A risk-benefit assessment of naltrexone in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Drug Saf. 1996;15:274–282. - PubMed
-
- Wellbutrin SR. GlaxoSmithKline; Research Triangle Park, NC: 2009. (bupropion hydrochloride) [package insert]
-
- Dhillon S, Yang LP, Curran MP. Bupropion: a review of its use in the management of major depressive disorder. Drugs. 2008;68:653–689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

