Intensive lifestyle intervention improves physical function among obese adults with knee pain: findings from the Look AHEAD trial
- PMID: 20559303
- PMCID: PMC3408003
- DOI: 10.1038/oby.2010.120
Intensive lifestyle intervention improves physical function among obese adults with knee pain: findings from the Look AHEAD trial
Erratum in
- Obesity (Silver Spring). 2011 Jan;19(1):233
Abstract
Lifestyle interventions have resulted in weight loss or improved physical fitness among individuals with obesity, which may lead to improved physical function. This prospective investigation involved participants in the Action for Health in Diabetes (Look AHEAD) trial who reported knee pain at baseline (n = 2,203). The purposes of this investigation were to determine whether an Intensive Lifestyle Intervention (ILI) condition resulted in improvement in self-reported physical function from baseline to 12 months vs. a Diabetes Support and Education (DSE) condition, and whether changes in weight or fitness mediated the effect of the ILI. Outcome measures included the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain, stiffness, and physical function subscales, and WOMAC summary score. ILI participants exhibited greater adjusted mean weight loss (s.e.) vs. DSE participants (-9.02 kg (0.48) vs. -0.78 kg (0.49); P < 0.001)). ILI participants also demonstrated more favorable change in WOMAC summary scores vs. DSE participants (β (s.e.) = -1.81 (0.63); P = 0.004). Multiple regression mediation analyses revealed that weight loss was a mediator of the effect of the ILI intervention on change in WOMAC pain, function, and summary scores (P < 0.001). In separate analyses, increased fitness also mediated the effect of the ILI intervention upon WOMAC summary score (P < 0.001). The ILI condition resulted in significant improvement in physical function among overweight and obese adults with diabetes and knee pain. The ILI condition also resulted in significant weight loss and improved fitness, which are possible mechanisms through which the ILI condition improved physical function.
Conflict of interest statement
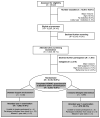
Figures



References
-
- Ogden CL, Yanovski SZ, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. The epidemiology of obesity. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2087–2102. - PubMed
-
- Field AE, Coakley EH, Must A, et al. Impact of overweight on the risk of developing common chronic diseases during a 10-year period. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161:1581–1586. - PubMed
-
- Chan JM, Rimm EB, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC. Obesity, fat distribution, and weight gain as risk factors for clinical diabetes in men. Diabetes Care. 1994;17:961–969. - PubMed
-
- Oguma Y, Sesso HD, Paffenbarger RS, Jr, Lee IM. Weight change and risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Obes Res. 2005;13:945–951. - PubMed
-
- Magliano M. Obesity and arthritis. Menopause Int. 2008;14:149–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- DK57078/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057151/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57151/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057136/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057002/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57178/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057177/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057078/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57135/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK048520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057135/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK046204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR002719/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057219/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK48520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR01066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57002/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR01346/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR000056 44/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- DK57136/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57219/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57177/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057178/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK56990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR0021140/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK 046204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR02719/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001346/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK56992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

