Further assembly required: construction and dynamics of the endoplasmic reticulum network
- PMID: 20559323
- PMCID: PMC2897125
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2010.92
Further assembly required: construction and dynamics of the endoplasmic reticulum network
Abstract
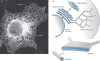
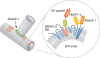
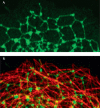
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a continuous membrane system comprising the nuclear envelope, ribosome-studded peripheral sheets and an interconnected network of smooth tubules extending throughout the cell. Although protein biosynthesis, transport and quality control in the ER have been studied extensively, mechanisms underlying the notably diverse architecture of the ER have only emerged recently; this review highlights these new findings and how they relate to ER functional specializations. Several protein families, including reticulons and DP1/REEPs/Yop1, harbour hydrophobic hairpin domains that shape high-curvature ER tubules and mediate intramembrane protein interactions. Members of the atlastin/RHD3/Sey1 family of dynamin-related GTPases mediate the formation of three-way junctions that characterize the tubular ER network, and additional classes of hydrophobic hairpin-containing ER proteins interact with and remodel the microtubule cytoskeleton. Flat ER sheets have a different complement of proteins implicated in shaping, cisternal stacking and microtubule interactions. Finally, several shaping proteins are mutated in hereditary spastic paraplegias, emphasizing the particular importance of proper ER morphology and distribution for highly polarized cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

