The habenula: from stress evasion to value-based decision-making
- PMID: 20559337
- PMCID: PMC3447364
- DOI: 10.1038/nrn2866
The habenula: from stress evasion to value-based decision-making
Abstract
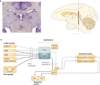
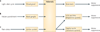
Surviving in a world with hidden rewards and dangers requires choosing the appropriate behaviours. Recent discoveries indicate that the habenula plays a prominent part in such behavioural choice through its effects on neuromodulator systems, in particular the dopamine and serotonin systems. By inhibiting dopamine-releasing neurons, habenula activation leads to the suppression of motor behaviour when an animal fails to obtain a reward or anticipates an aversive outcome. Moreover, the habenula is involved in behavioural responses to pain, stress, anxiety, sleep and reward, and its dysfunction is associated with depression, schizophrenia and drug-induced psychosis. As a highly conserved structure in the brain, the habenula provides a fundamental mechanism for both survival and decision-making.
Figures

References
-
- Dadda M, Domenichini A, Piffer L, Argenton F, Bisazza A. Early differences in epithalamic left–right asymmetry influence lateralization and personality of adult zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2010;206:208–215. - PubMed
-
- Guglielmotti V, Cristino L. The interplay between the pineal complex and the habenular nuclei in lower vertebrates in the context of the evolution of cerebral asymmetry. Brain Res. Bull. 2006;69:475–488. - PubMed
-
- Ronnekleiv OK, Moller M. Brain-pineal nervous connections in the rat: an ultrastructure study following habenular lesion. Exp. Brain Res. 1979;37:551–562. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

