Plasmacytoid dendritic cells accumulate and secrete interferon alpha in lymph nodes of HIV-1 patients
- PMID: 20559432
- PMCID: PMC2885422
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011110
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells accumulate and secrete interferon alpha in lymph nodes of HIV-1 patients
Abstract
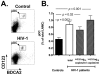
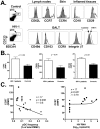
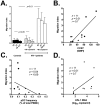
Circulating plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC) decline during HIV-1 infection, but at the same time they express markedly higher levels of interferon alpha (IFNalpha), which is associated with HIV-1 disease progression. Here we show an accumulation of pDC in lymph nodes (LN) of treatment-naïve HIV-1 patients. This phenomenon was associated with elevated expression of the LN homing marker, CCR7, on pDC in peripheral blood of HIV-1 patients, which conferred increased migratory capacity in response to CCR7 ligands in ex vivo functional assays. LN-homed pDC of HIV-1 patients presented higher CD40 and lower BDCA2 levels, but unchanged CD83 and CD86 expression. In addition, these cells expressed markedly higher amounts of IFNalpha compared to uninfected individuals, and were undergoing faster rates of cell death. These results demonstrate for the first time that in asymptomatic, untreated HIV-1 patients circulating pDC up-regulate CCR7 expression, accumulate in lymph nodes, and express high amounts of IFNalpha before undergoing cell death. Since IFNalpha inhibits cell proliferation and modulates immune responses, chronically high levels of this cytokine in LN of HIV-1 patients may impair differentiation and immune function of bystander CD4(+) T cells, thus playing into the mechanisms of AIDS immunopathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
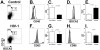
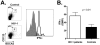
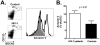
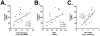
Similar articles
-
Impaired CCR7 expression on plasmacytoid dendritic cells of HIV-infected children and adolescents with immunologic and virologic failure.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007 Aug 15;45(5):501-7. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3180654811. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007. PMID: 17468665
-
Increased interferon alpha expression in circulating plasmacytoid dendritic cells of HIV-1-infected patients.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2008 Aug 15;48(5):522-30. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e31817f97cf. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2008. PMID: 18645522
-
Lymph nodes from HIV-infected individuals harbor mature dendritic cells and increased numbers of PD-L1+ conventional dendritic cells.Hum Immunol. 2016 Jul;77(7):584-93. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2016.05.019. Epub 2016 May 21. Hum Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27221659
-
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells in HIV infection: striking a delicate balance.J Leukoc Biol. 2010 Apr;87(4):609-20. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0909635. Epub 2010 Feb 9. J Leukoc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20145197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV-1 immunopathogenesis: how good interferon turns bad.Clin Immunol. 2007 May;123(2):121-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2006.09.016. Epub 2006 Nov 16. Clin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17112786 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells in HIV infection.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;762:71-107. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4433-6_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 22975872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dendritic cell dysregulation during HIV-1 infection.Immunol Rev. 2013 Jul;254(1):170-89. doi: 10.1111/imr.12082. Immunol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23772620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue-specific interferon alpha subtype response to SIV infection in brain, spleen, and lung.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013 Jan;33(1):24-33. doi: 10.1089/jir.2012.0018. Epub 2012 Oct 10. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013. PMID: 23050948 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient infection, activation, and impairment of pDCs in the BM and peripheral lymphoid organs during early HIV-1 infection in humanized rag2⁻/⁻γ C⁻/⁻ mice in vivo.Blood. 2011 Jun 9;117(23):6184-92. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-331173. Epub 2011 Apr 19. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21505190 Free PMC article.
-
Type I Interferon Responses by HIV-1 Infection: Association with Disease Progression and Control.Front Immunol. 2018 Jan 15;8:1823. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01823. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29379496 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fahey JL, Taylor JM, Detels R, Hofmann B, Melmed R, et al. The prognostic value of cellular and serologic markers in infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:166–172. - PubMed
-
- Giorgi JV, Liu Z, Hultin LE, Cumberland WG, Hennessey K, et al. Elevated levels of CD38+ CD8+ T cells in HIV infection add to the prognostic value of low CD4+ T cell levels: results of 6 years of follow-up. The Los Angeles Center, Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1993;6:904–912. - PubMed
-
- Deeks SG, Kitchen CM, Liu L, Guo H, Gascon R, et al. Immune activation set point during early HIV infection predicts subsequent CD4+ T-cell changes independent of viral load. Blood. 2004;104:942–947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

