On the chemistry, toxicology and genetics of the cyanobacterial toxins, microcystin, nodularin, saxitoxin and cylindrospermopsin
- PMID: 20559491
- PMCID: PMC2885083
- DOI: 10.3390/md8051650
On the chemistry, toxicology and genetics of the cyanobacterial toxins, microcystin, nodularin, saxitoxin and cylindrospermopsin
Abstract
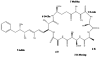
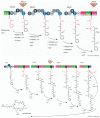
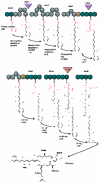
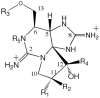
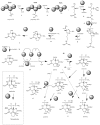
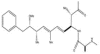
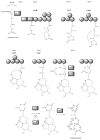
The cyanobacteria or "blue-green algae", as they are commonly termed, comprise a diverse group of oxygenic photosynthetic bacteria that inhabit a wide range of aquatic and terrestrial environments, and display incredible morphological diversity. Many aquatic, bloom-forming species of cyanobacteria are capable of producing biologically active secondary metabolites, which are highly toxic to humans and other animals. From a toxicological viewpoint, the cyanotoxins span four major classes: the neurotoxins, hepatotoxins, cytotoxins, and dermatoxins (irritant toxins). However, structurally they are quite diverse. Over the past decade, the biosynthesis pathways of the four major cyanotoxins: microcystin, nodularin, saxitoxin and cylindrospermopsin, have been genetically and biochemically elucidated. This review provides an overview of these biosynthesis pathways and additionally summarizes the chemistry and toxicology of these remarkable secondary metabolites.
Keywords: alkaloid; cyanotoxin; non-ribosomal peptide; polyketide; toxicology.
Figures




References
-
- Sivonen K, Jones G. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health consequences, Monitoring and Management. Vol. 1. E and FN Spon; New York, NY, USA: 1999. pp. 40–111.
-
- Welker M, von Dohren H. Cyanobacterial peptides -nature’s own combinatorial biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2006;30:530–563. - PubMed
-
- Botes D, Wessels P, Kruger H, Runnegar M, Santikarn S, Smith R, Barna J, Williams D. Structural studies on cyanoginosins-LR, -YR, -YA, and -YM, peptide toxins from Microcystis aeruginosa. J Chem Soc. 1985;1:2747–2748.
-
- Namikoshi M, Yuan M, Sivonen K, Carmichael WW, Rinehart KL, Rouhiainen L, Sun F, Brittain S, Otsuki A. Seven new microcystins possessing two l-glutamic acid units, isolated from Anabaena sp. strain 186. Chem Res Toxicol. 1998;11:143–149. - PubMed
-
- Rinehart K, Namikoshi N, Choi B. Structure and biosynthesis of toxins from blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) J App Phycol. 1994;6:159–176.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
