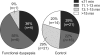The speed of eating and functional dyspepsia in young women
- PMID: 20559518
- PMCID: PMC2886943
- DOI: 10.5009/gnl.2010.4.2.173
The speed of eating and functional dyspepsia in young women
Abstract
Background/aims: Little information is available on whether the speed of eating differs between individuals with and without dyspepsia, mainly because controlled studies are usually not feasible.
Methods: A survey was applied to 89 individuals with relatively controlled eating patterns, using questionnaires that assessed eating time and functional dyspepsia (FD) based on the Rome III criteria.
Results: The prevalence of FD was 12% (11 of 89 participants), and 7% (6 of 89) were diagnosed with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The proportion of individuals reporting that they ate their meals rapidly was higher for those with FD than for those without FD or GERD (control) (46% vs 17%, p=0.043), as was the reported eating speed (7.1+/-1.5 vs 5.8+/-2.0 [mean+/-SD], p=0.045; visual analog scale on which a higher score indicated faster eating). However, the measured eating time did not differ significantly between FD and controls (11.0+/-2.8 vs 12.8+/-3.3 minutes, p=0.098). The proportion of individuals who ate their meals within 13 minutes was significantly higher for those with FD than for controls (91% vs 51%, p=0.020).
Conclusions: The results of this study suggest that eating speed affects dyspepsia. Further studies are warranted.
Keywords: Diet habits; Eating speed; Functional dyspepsia.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial support, None. Potential competing interests, None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association Between Eating Behavior, Frequency of Meals, and Functional Dyspepsia in Young Japanese Population.J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2022 Jul 30;28(3):418-423. doi: 10.5056/jnm21146. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2022. PMID: 35799235 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between Tooth Loss, Functional Dyspepsia and Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disorder among Isfahani Adults.Arch Iran Med. 2016 Feb;19(2):123-30. Arch Iran Med. 2016. PMID: 26838083
-
Overlap of symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease, dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome in the general population.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb;50(2):162-9. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2014.983157. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25525975
-
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease-Functional Dyspepsia Overlap: Do Birds of a Feather Flock Together?Am J Gastroenterol. 2020 Aug;115(8):1167-1182. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000619. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32453043
-
Food and functional dyspepsia: a systematic review.J Hum Nutr Diet. 2018 Jun;31(3):390-407. doi: 10.1111/jhn.12506. Epub 2017 Sep 15. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2018. PMID: 28913843
Cited by
-
Food, Dietary Patterns, or Is Eating Behavior to Blame? Analyzing the Nutritional Aspects of Functional Dyspepsia.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 22;15(6):1544. doi: 10.3390/nu15061544. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36986274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association Between Eating Behavior, Frequency of Meals, and Functional Dyspepsia in Young Japanese Population.J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2022 Jul 30;28(3):418-423. doi: 10.5056/jnm21146. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2022. PMID: 35799235 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Diet in Functional Dyspepsia Management.Front Psychiatry. 2020 Feb 5;11:23. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00023. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32116840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of eating habits with health perception and diseases among Chinese physicians: a cross-sectional study.Front Nutr. 2023 Aug 11;10:1226672. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1226672. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37637951 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Bojanggunbi-tang and its primary constituent herbs on the gastrointestinal tract: a scoping review.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 12;16:1543194. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1543194. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40144663 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feinle-Bisset C, Horowitz M. Dietary factors in functional dyspepsia. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2006;18:608–618. - PubMed
-
- Mullan A, Kavanagh P, O'Mahony P, Joy T, Gleeson F, Gibney MJ. Food and nutrient intakes and eating patterns in functional and organic dyspepsia. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1994;48:97–105. - PubMed
-
- Feinle-Bisset C, Vozzo R, Horowitz M, Talley NJ. Diet, food intake, and disturbed physiology in the pathogenesis of symptoms in functional dyspepsia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99:170–181. - PubMed
-
- Cuperus P, Keeling PW, Gibney MJ. Eating patterns in functional dyspepsia: a case control study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1996;50:520–523. - PubMed
-
- Tack J, Talley NJ, Camilleri M, et al. Functional gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1466–1479. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials