Development of an automated microfluidic reaction platform for multidimensional screening: reaction discovery employing bicyclo[3.2.1]octanoid scaffolds
- PMID: 20560568
- PMCID: PMC2976622
- DOI: 10.1021/jo901073v
Development of an automated microfluidic reaction platform for multidimensional screening: reaction discovery employing bicyclo[3.2.1]octanoid scaffolds
Abstract
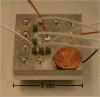
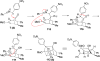
An automated, silicon-based microreactor system has been developed for rapid, low-volume, multidimensional reaction screening. Use of the microfluidic platform to identify transformations of densely functionalized bicyclo[3.2.1]octanoid scaffolds will be described.
Figures











References
-
- Balamurugan R, Dekker FJ, Waldmann H. Mol BioSyst. 2005;1:36. - PubMed
- Arve L, Voigt T, Waldmann H. QSAR Comb Sci. 2006;25:449.
-
- Schreiber SL. Science. 2000;287:1964. - PubMed
- Tan DS. Nat Chem Biol. 2005;1:74. - PubMed
- Shang S, Tan DS. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2005;9:248. - PubMed
- Wipf P, Coleman CM, Janjic JM, Iyer PS, Fodor MD, Shafer YA, Stephenson CRJ, Kendall C, Day BW. J Comb Chem. 2005;7:322. - PubMed
- Wipf P, Werner S, Woo GHC, Stephenson CRJ, Walczak MAA, Coleman CM, Twining LA. Tetrahedron. 2005;61:11488.
- Thomas GL, Wyatt EE, Spring DR. Curr Opin Drug Discovery Dev. 2006;9:700. - PubMed
- Spandl RJ, Bender A, Spring DR. Org Biomol Chem. 2008;6:1149. - PubMed
-
- Beeler AB, Su S, Singleton CA, Porco JA., Jr J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:1413. - PubMed
-
-
For discussion of reaction screening approaches, see: Weber L, Illgen K, Almstetter M. Synlett. 1999:366.Kana WM, Rosenman MM, Sakurai K, Snyder TM, Liu DR. Nature. 2004;431:545.Miller SJ. Nat Biotechnol. 2004;22:1378.
-
-
- Liu B, Li S, Hu J. Am J Pharmacogenomics. 2004;4:263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

