STIM proteins: integrators of signalling pathways in development, differentiation and disease
- PMID: 20561111
- PMCID: PMC3823271
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01097.x
STIM proteins: integrators of signalling pathways in development, differentiation and disease
Abstract
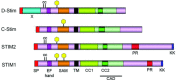
The stromal interaction molecules STIM1 and STIM2 are endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) sensors, serving to detect changes in receptor-mediated ER Ca(2+) store depletion and to relay this information to plasma membrane localized proteins, including the store-operated Ca(2+) channels of the ORAI family. The resulting Ca(2+) influx sustains the high cytosolic Ca(2+) levels required for activation of many intracellular signal transducers such as the NFAT family of transcription factors. Models of STIM protein deficiency in mice, Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans, in addition to the phenotype of patients bearing mutations in STIM1 have provided great insight into the role of these proteins in cell physiology and pathology. It is now becoming clear that STIM1 and STIM2 are critical for the development and functioning of many cell types, including lymphocytes, skeletal and smooth muscle myoblasts, adipocytes and neurons, and can interact with a variety of signalling proteins and pathways in a cell- and tissue-type specific manner. This review focuses on the role of STIM proteins in development, differentiation and disease, in particular highlighting the functional differences between STIM1 and STIM2.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human muscle economy myoblast differentiation and excitation-contraction coupling use the same molecular partners, STIM1 and STIM2.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 16;285(29):22437-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.118984. Epub 2010 May 1. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20436167 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of stromal interaction molecules.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Mar;243(5):451-472. doi: 10.1177/1535370218754524. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 29363328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STIM1 and STIM2 proteins differently regulate endogenous store-operated channels in HEK293 cells.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 20;290(8):4717-4727. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.601856. Epub 2014 Dec 22. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25533457 Free PMC article.
-
The STIM/Orai coupling machinery.Channels (Austin). 2008 Jul-Aug;2(4):261-8. doi: 10.4161/chan.2.4.6705. Epub 2008 Jul 21. Channels (Austin). 2008. PMID: 18769136 Review.
-
Identification and characterization of the STIM (stromal interaction molecule) gene family: coding for a novel class of transmembrane proteins.Biochem J. 2001 Aug 1;357(Pt 3):673-85. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3570673. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11463338 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Fructus Corni extract-induced neuritogenesis in PC12 cells is associated with the suppression of stromal interaction molecule 1 expression and inhibition of Ca2+ influx.Exp Ther Med. 2015 May;9(5):1773-1779. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2316. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Exp Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 26136892 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of Stim1 at serine 575 via netrin-2/Cdo-activated ERK1/2 is critical for the promyogenic function of Stim1.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Apr;23(7):1376-87. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-07-0634. Epub 2012 Feb 1. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22298426 Free PMC article.
-
A cytosolic STIM2 preprotein created by signal peptide inefficiency activates ORAI1 in a store-independent manner.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 6;286(18):16174-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.206946. Epub 2011 Mar 7. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21383014 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium signaling in lacrimal glands.Cell Calcium. 2014 Jun;55(6):290-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2014.01.001. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Cell Calcium. 2014. PMID: 24507443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Store-operated Ca2+ entry is remodelled and controls in vitro angiogenesis in endothelial progenitor cells isolated from tumoral patients.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e42541. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042541. Epub 2012 Sep 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23049731 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Petersen OH, Tepikin AV, Gerasimenko JV, et al. Fatty acids, alcohol and fatty acid ethyl esters: toxic Ca2+ signal generation and pancreatitis. Cell Calcium. 2009;45:634–42. - PubMed
-
- Lebeche D, Davidoff AJ, Hajjar RJ. Interplay between impaired calcium regulation and insulin signaling abnormalities in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2008;5:715–24. - PubMed
-
- Mohan CG, Gandhi T. Therapeutic potential of voltage gated calcium channels. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008;8:1285–90. - PubMed
-
- Ferraccioli GF, Tomietto P, De Santis M. Rationale for T cell inhibition by cyclosporin A in major autoimmune diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1051:658–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

