STIM proteins: integrators of signalling pathways in development, differentiation and disease
- PMID: 20561111
- PMCID: PMC3823271
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01097.x
STIM proteins: integrators of signalling pathways in development, differentiation and disease
Abstract
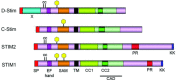
The stromal interaction molecules STIM1 and STIM2 are endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) sensors, serving to detect changes in receptor-mediated ER Ca(2+) store depletion and to relay this information to plasma membrane localized proteins, including the store-operated Ca(2+) channels of the ORAI family. The resulting Ca(2+) influx sustains the high cytosolic Ca(2+) levels required for activation of many intracellular signal transducers such as the NFAT family of transcription factors. Models of STIM protein deficiency in mice, Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans, in addition to the phenotype of patients bearing mutations in STIM1 have provided great insight into the role of these proteins in cell physiology and pathology. It is now becoming clear that STIM1 and STIM2 are critical for the development and functioning of many cell types, including lymphocytes, skeletal and smooth muscle myoblasts, adipocytes and neurons, and can interact with a variety of signalling proteins and pathways in a cell- and tissue-type specific manner. This review focuses on the role of STIM proteins in development, differentiation and disease, in particular highlighting the functional differences between STIM1 and STIM2.
Figures

References
-
- Petersen OH, Tepikin AV, Gerasimenko JV, et al. Fatty acids, alcohol and fatty acid ethyl esters: toxic Ca2+ signal generation and pancreatitis. Cell Calcium. 2009;45:634–42. - PubMed
-
- Lebeche D, Davidoff AJ, Hajjar RJ. Interplay between impaired calcium regulation and insulin signaling abnormalities in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2008;5:715–24. - PubMed
-
- Mohan CG, Gandhi T. Therapeutic potential of voltage gated calcium channels. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008;8:1285–90. - PubMed
-
- Ferraccioli GF, Tomietto P, De Santis M. Rationale for T cell inhibition by cyclosporin A in major autoimmune diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1051:658–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

