Specific resistances against Pseudomonas syringae effectors AvrB and AvrRpm1 have evolved differently in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris), soybean (Glycine max), and Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 20561214
- PMCID: PMC2922445
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03337.x
Specific resistances against Pseudomonas syringae effectors AvrB and AvrRpm1 have evolved differently in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris), soybean (Glycine max), and Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
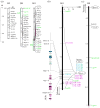
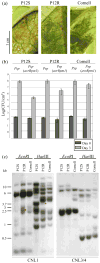
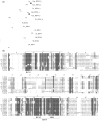
*In plants, the evolution of specific resistance is poorly understood. Pseudomonas syringae effectors AvrB and AvrRpm1 are recognized by phylogenetically distinct resistance (R) proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana (Brassicaceae) and soybean (Glycine max, Fabaceae). In soybean, these resistances are encoded by two tightly linked R genes, Rpg1-b and Rpg1-r. To study the evolution of these specific resistances, we investigated AvrB- and AvrRpm1-induced responses in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris, Fabaceae). *Common bean genotypes of various geographical origins were inoculated with P. syringae strains expressing AvrB or AvrRpm1. A common bean recombinant inbred line (RIL) population was used to map R genes to AvrRpm1. *No common bean genotypes recognized AvrB. By contrast, multiple genotypes responded to AvrRpm1, and two independent R genes conferring AvrRpm1-specific resistance were mapped to the ends of linkage group B11 (Rpsar-1, for resistance to Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrRpm1 number 1) and B8 (Rpsar-2). Rpsar-1 is located in a region syntenic with the soybean Rpg1 cluster. However, mapping of specific Rpg1 homologous genes suggests that AvrRpm1 recognition evolved independently in common bean and soybean. *The conservation of the genomic position of AvrRpm1-specific genes between soybean and common bean suggests a model whereby specific clusters of R genes are predisposed to evolve recognition of the same effector molecules.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evolutionary relationship of disease resistance genes in soybean and Arabidopsis specific for the Pseudomonas syringae effectors AvrB and AvrRpm1.Plant Physiol. 2014 Sep;166(1):235-51. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.244715. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Plant Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25034017 Free PMC article.
-
RPG1-B-derived resistance to AvrB-expressing Pseudomonas syringae requires RIN4-like proteins in soybean.Plant Physiol. 2010 Jul;153(3):1199-211. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.158147. Epub 2010 May 18. Plant Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20484023 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas syringae Effector AvrPphB Suppresses AvrB-Induced Activation of RPM1 but Not AvrRpm1-Induced Activation.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2015 Jun;28(6):727-35. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-08-14-0248-R. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2015. PMID: 25625821
-
Arabidopsis TAO1 is a TIR-NB-LRR protein that contributes to disease resistance induced by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrB.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 29;105(17):6475-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802157105. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18424557 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola: from 'has bean' to supermodel.Mol Plant Pathol. 2011 Sep;12(7):617-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2010.00697.x. Epub 2011 Feb 17. Mol Plant Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21726364 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic mapping of two genes conferring resistance to powdery mildew in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2013 Jun;126(6):1503-12. doi: 10.1007/s00122-013-2068-y. Epub 2013 Mar 3. Theor Appl Genet. 2013. PMID: 23456179
-
Dissection of Resistance Genes to Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola in UI3 Common Bean Cultivar.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 23;18(12):2503. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122503. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29168746 Free PMC article.
-
Pattern Recognition Receptors in Plant Immunity.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1476:425-451. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-85340-1_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40622553 Review.
-
Fine mapping of Co-x, an anthracnose resistance gene to a highly virulent strain of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum in common bean.Theor Appl Genet. 2014 Jul;127(7):1653-66. doi: 10.1007/s00122-014-2328-5. Epub 2014 May 25. Theor Appl Genet. 2014. PMID: 24859268
-
Comparative analysis of NBS-LRR genes and their response to Aspergillus flavus in Arachis.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 3;12(2):e0171181. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171181. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28158222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam-Blondon AF. thesis. INAPG; 1994. Cartographie génétique de Phaseolus vulgaris L. localisation de gènes de résistance à l’anthracnose; p. 160.
-
- Ashfield T, Bocian A, Held D, Henk AD, Marek LF, Danesh D, Penuela S, Meksem K, Lightfoot DA, Young ND, et al. Genetic and physical localization of the soybean Rpg1-b disease resistance gene reveals a complex locus containing several tightly linked families of NBS-LRR genes. Molecular Plant Microbe Interactions. 2003;16:817–826. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

