Serotonin: a regulator of neuronal morphology and circuitry
- PMID: 20561690
- PMCID: PMC2929308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2010.05.005
Serotonin: a regulator of neuronal morphology and circuitry
Abstract
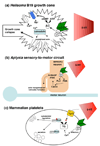
Serotonin is an important neuromodulator associated with a wide range of physiological effects in the central nervous system. The exact mechanisms whereby serotonin influences brain development are not well understood, although studies in invertebrate and vertebrate model organisms are beginning to unravel a regulatory role for serotonin in neuronal morphology and circuit formation. Recent data suggest a developmental window during which altered serotonin levels permanently influence neuronal circuitry, however, the temporal constraints and molecular mechanisms responsible are still under investigation. Growing evidence suggests that alterations in early serotonin signaling contribute to a number of neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders. Thus, understanding how altered serotonin signaling affects neuronal morphology and plasticity, and ultimately animal physiology and pathophysiology, will be of great significance.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative localization of two serotonin receptors and sensorin in the central nervous system of Aplysia californica.J Comp Neurol. 2005 Sep 26;490(3):295-304. doi: 10.1002/cne.20666. J Comp Neurol. 2005. PMID: 16082675
-
Serotonin in the modulation of neural plasticity and networks: implications for neurodevelopmental disorders.Neuron. 2012 Oct 4;76(1):175-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.013. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 23040814 Review.
-
Modulation of the serotonin system by endocannabinoid signaling.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Sep;61(3):414-20. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.02.016. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21354188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin and prefrontal cortex function: neurons, networks, and circuits.Mol Neurobiol. 2011 Dec;44(3):449-64. doi: 10.1007/s12035-011-8214-0. Epub 2011 Nov 11. Mol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 22076606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distribution of serotonin-like immunoreactive neurons in the slug Limax valentianus.Cell Tissue Res. 2004 Feb;315(2):285-90. doi: 10.1007/s00441-003-0820-3. Epub 2003 Nov 26. Cell Tissue Res. 2004. PMID: 14648193
Cited by
-
Activation of 5-HT7 receptor stimulates neurite elongation through mTOR, Cdc42 and actin filaments dynamics.Front Behav Neurosci. 2015 Mar 11;9:62. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00062. eCollection 2015. Front Behav Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25814944 Free PMC article.
-
Scaling Our World View: How Monoamines Can Put Context Into Brain Circuitry.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Dec 20;12:506. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00506. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30618646 Free PMC article.
-
Light-activated serotonin for exploring its action in biological systems.Chem Biol. 2013 Dec 19;20(12):1536-46. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.11.005. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 24333002 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Prenatal Cannabinoids Exposure upon Placenta and Development of Respiratory Neural Circuits.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1428:199-232. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-32554-0_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37466775 Review.
-
In vivo relationship between serotonin 1A receptor binding and gray matter volume in the healthy brain and in major depressive disorder.Brain Struct Funct. 2018 Jul;223(6):2609-2625. doi: 10.1007/s00429-018-1649-6. Epub 2018 Mar 17. Brain Struct Funct. 2018. PMID: 29550938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Serfaty CA, et al. Nutritional tryptophan restriction and the role of serotonin in development and plasticity of central visual connections. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2008;15:170–175. - PubMed
-
- Papaioannou A, et al. Effects of neonatal handling on basal and stress-induced monoamine levels in the male and female brain. Neuroscience. 2002;114:195–206. - PubMed
-
- Winter C, et al. Prenatal immune activation leads to multiple changes in basal neurotransmitter levels in the adult brain: implications for brain disorders of neurodevelopmental origin such as schizophrenia. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009;12:513–524. - PubMed
-
- Xu Y, et al. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor disrupts organization of thalamocortical somatosensory barrels during development. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 2004;150:151–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

