The twists and turns of sphingolipid pathway in glucose regulation
- PMID: 20561942
- PMCID: PMC3006650
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biochi.2010.05.016
The twists and turns of sphingolipid pathway in glucose regulation
Abstract
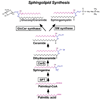
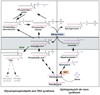
Palmitic acid is a saturated fat found in foods that lead to obesity, cardiovascular disease, and Type II diabetes. It is linked to the development of resistance to insulin stimulation in muscle, liver and other organs involved in glucose metabolism, which, in turn, underlines the onset of Type II diabetes. The cellular and molecular mechanisms of this insulin resistance are complex and not completely understood. This article is focused on the role of palmitic acid as a precursor in the synthesis of sphingolipids, a class of lipid molecules that participate in cellular stress response. Recent evidence had indicated that increased dietary supply of palmitate can stimulate the rate of sphingolipid synthesis in "lean" tissues and generate excessive amounts of sphingolipid metabolites that have a negative effect on the insulin signaling cascade. Many experimental results point to the existence of a causative link between sphingolipid synthesis, insulin response, and hyperglycemia. It is not yet clear, however whether ceramides or glycosphingolipids are involved as both have been implicated to be inhibitors of the insulin signaling cascade. Evidence for a coordinated regulation of sphingolipid and tri/diacylglycerol metabolism complicates further the delineation of a single mechanism of sphingolipid effect on glucose homeostasis.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sphingolipids as a Culprit of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 18;12:635175. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.635175. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33815291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingolipid Metabolism: New Insight into Ceramide-Induced Lipotoxicity in Muscle Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 23;20(3):479. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030479. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30678043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidants Supplementation Reduces Ceramide Synthesis Improving the Cardiac Insulin Transduction Pathway in a Rodent Model of Obesity.Nutrients. 2021 Sep 28;13(10):3413. doi: 10.3390/nu13103413. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34684414 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of ceramide synthesis ameliorates glucocorticoid-, saturated-fat-, and obesity-induced insulin resistance.Cell Metab. 2007 Mar;5(3):167-79. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.01.002. Cell Metab. 2007. PMID: 17339025
-
Metabolism and insulin signaling in common metabolic disorders and inherited insulin resistance.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4890. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123125 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of intramyocelluar lipids in human health.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Aug;23(8):391-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.05.009. Epub 2012 Jun 20. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22721584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TNF-α- and tumor-induced skeletal muscle atrophy involves sphingolipid metabolism.Skelet Muscle. 2012 Jan 18;2(1):2. doi: 10.1186/2044-5040-2-2. Skelet Muscle. 2012. PMID: 22257771 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted sphingolipid metabolism following acute clozapine and olanzapine administration.J Biomed Sci. 2018 May 2;25(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12929-018-0437-1. J Biomed Sci. 2018. PMID: 29720183 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma deoxysphingolipids: a novel class of biomarkers for the metabolic syndrome?Diabetologia. 2012 Feb;55(2):421-31. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2384-1. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22124606
-
Lipidomics in Biomarker Research.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022;270:493-510. doi: 10.1007/164_2021_517. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34409495 Review.
References
-
- den Boer M, Voshol PJ, Kuipers F, Havekes LM, Romijn JA. Hepatic Steatosis: A Mediator of the Metabolic Syndrome. Lessons From Animal Models. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:644–649. - PubMed
-
- Riserus U. Fatty acids and insulin sensitivity. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2008;11:100–105. - PubMed
-
- Galgani JE, Uauy RD, Aguirre CA, Díaz EO. Effect of the dietary fat quality on insulin sensitivity. British Journal of Nutrition. 2008;100:471–479. - PubMed
-
- Samad F, Hester KD, Yang G, Hannun YA, Bielawski J. Altered adipose and plasma sphingolipid metabolism in obesity: a potential mechanism for cardiovascular and metabolic risk. Diabetes. 2006;55:2579–2587. - PubMed
-
- Straczkowski M, Kowalska I, Baranowski M, Nikolajuk A, Otziomek E, Zabielski P, Adamska A, Blachnio A, Gorski J, Gorska M. Increased skeletal muscle ceramide level in men at risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2007;50:2366–2373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

