Inhibition of STAT3 signaling blocks the anti-apoptotic activity of IL-6 in human liver cancer cells
- PMID: 20562100
- PMCID: PMC2930741
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.142752
Inhibition of STAT3 signaling blocks the anti-apoptotic activity of IL-6 in human liver cancer cells
Abstract
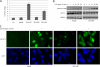
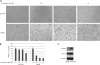
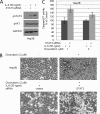
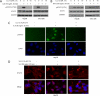
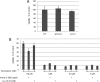
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a multifunctional cytokine, which may block apoptosis during inflammation to protect cells under very toxic conditions. However, IL-6 also activates STAT3 in many types of human cancer. Recent studies demonstrate that high levels of IL-6 are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma, the most common type of liver cancer. Here we reported that IL-6 promoted survival of human liver cancer cells through activating STAT3 in response to doxorubicin treatment. Endogenous IL-6 levels in SNU-449 cells were higher than in Hep3B cells. Meanwhile, SNU-449 cells were more resistant to doxorubicin than Hep3B cells. Addition of IL-6 induced STAT3 activation in Hep3B cells and led to protection against doxorubicin. In contrast, neutralizing IL-6 with anti-IL-6 antibody decreased survival of SNU-449 cells in response to doxorubicin. To elucidate the mechanism of the anti-apoptotic function of IL-6, we investigated if STAT3 mediated this drug resistance. Targeting STAT3 with STAT3 siRNA reduced the protection of IL-6 against doxorubicin-induced apoptosis, indicating that STAT3 signaling contributed to the anti-apoptotic effect of IL-6. Moreover, we further explored if a STAT3 small molecule inhibitor could abolish this anti-apoptotic effect. LLL12, a STAT3 small molecule inhibitor, blocked IL-6-induced STAT3 phosphorylation, resulting in attenuation of the anti-apoptotic activity of IL-6. Finally, neutralization of endogenous IL-6 with anti-IL-6 antibody or blockade of STAT3 with LLL12 lowered the recovery in SNU-449 cells after doxorubicin treatment. Therefore, our results demonstrated that targeting STAT3 signaling could interrupt the anti-apoptotic function of IL-6 in human liver cancer cells.
Figures


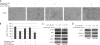

Similar articles
-
LLL12, a novel small inhibitor targeting STAT3 for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy.Oncotarget. 2015 May 10;6(13):10940-9. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3458. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25883212 Free PMC article.
-
A small molecule, LLL12 inhibits constitutive STAT3 and IL-6-induced STAT3 signaling and exhibits potent growth suppressive activity in human multiple myeloma cells.Int J Cancer. 2012 Mar 15;130(6):1459-69. doi: 10.1002/ijc.26152. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Int J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 21520044 Free PMC article.
-
IL-6, a risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma: FLLL32 inhibits IL-6-induced STAT3 phosphorylation in human hepatocellular cancer cells.Cell Cycle. 2010 Sep 1;9(17):3423-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.17.12946. Epub 2010 Sep 8. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20818158
-
17β-estradiol exerts anticancer effects in anoikis-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines by targeting IL-6/STAT3 signaling.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 May 13;473(4):1247-1254. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.04.049. Epub 2016 Apr 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27091428
-
Interleukin-6 at the Host-Tumor Interface: STAT3 in Biomolecular Condensates in Cancer Cells.Cells. 2022 Mar 30;11(7):1164. doi: 10.3390/cells11071164. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406728 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reposition of the anti-inflammatory drug diacerein in an in-vivo colorectal cancer model.Saudi Pharm J. 2022 Jan;30(1):72-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2021.12.009. Epub 2021 Dec 31. Saudi Pharm J. 2022. PMID: 35145347 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the IL-6-Signaling Pathway in Liver Cells by miRNAs Targeting gp130, JAK1, and/or STAT3.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019 Jun 7;16:419-433. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.03.007. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019. PMID: 31026677 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of interleukin-21 in the regulation of colitis-associated colon cancer.J Exp Med. 2011 Oct 24;208(11):2279-90. doi: 10.1084/jem.20111106. Epub 2011 Oct 10. J Exp Med. 2011. PMID: 21987656 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein-induced SH2 domain-containing 5 (SH2D5) expression promotes hepatoma cell growth via an SH2D5-transketolase interaction.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 29;294(13):4815-4827. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005739. Epub 2019 Jan 18. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30659097 Free PMC article.
-
Role of miRNA let-7 and its major targets in prostate cancer.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:376326. doi: 10.1155/2014/376326. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25276782 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

