Up-regulation of the homophilic adhesion molecule sidekick-1 in podocytes contributes to glomerulosclerosis
- PMID: 20562105
- PMCID: PMC2919131
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.133959
Up-regulation of the homophilic adhesion molecule sidekick-1 in podocytes contributes to glomerulosclerosis
Abstract
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a leading cause of nephrotic syndrome and end-stage renal disease worldwide. Although the mechanisms underlying this important disease are poorly understood, the glomerular podocyte clearly plays a central role in disease pathogenesis. In the current work, we demonstrate that the homophilic adhesion molecule sidekick-1 (sdk-1) is up-regulated in podocytes in FSGS both in rodent models and in human kidney biopsy samples. Transgenic mice that have podocyte-specific overexpression of sdk-1 develop gradually progressive heavy proteinuria and severe FSGS. We also show that sdk-1 associates with the slit diaphragm linker protein MAGI-1, which is already known to interact with several critical podocyte proteins including synaptopodin, alpha-actinin-4, nephrin, JAM4, and beta-catenin. This interaction is mediated through a direct interaction between the carboxyl terminus of sdk-1 and specific PDZ domains of MAGI-1. In vitro expression of sdk-1 enables a dramatic recruitment of MAGI-1 to the cell membrane. Furthermore, a truncated version of sdk-1 that is unable to bind to MAGI-1 does not induce podocyte dysfunction when overexpressed. We conclude that the up-regulation of sdk-1 in podocytes is an important pathogenic factor in FSGS and that the mechanism involves disruption of the actin cytoskeleton possibly via alterations in MAGI-1 function.
Figures
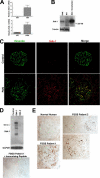
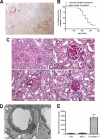



Similar articles
-
MAGI-1 Interacts with Nephrin to Maintain Slit Diaphragm Structure through Enhanced Rap1 Activation in Podocytes.J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 18;291(47):24406-24417. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.745026. Epub 2016 Oct 5. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27707879 Free PMC article.
-
MAGI-1 is a component of the glomerular slit diaphragm that is tightly associated with nephrin.Lab Invest. 2005 Dec;85(12):1528-43. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.3700347. Lab Invest. 2005. PMID: 16155592
-
Glomerulosclerosis Induced by Deficiency of Membrane-Associated Guanylate Kinase Inverted 2 in Kidney Podocytes.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Sep;28(9):2654-2669. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016121356. Epub 2017 May 24. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28539383 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of TRPC6 ion channels in podocytes - Implications for focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and acquired forms of proteinuric diseases.Acta Physiol Hung. 2015 Sep;102(3):241-51. doi: 10.1556/036.102.2015.3.2. Acta Physiol Hung. 2015. PMID: 26551740 Review.
-
TRPC6 and FSGS: the latest TRP channelopathy.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Aug;1772(8):859-68. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2007.03.005. Epub 2007 Mar 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17459670 Review.
Cited by
-
The PDZ3 domain of the cellular scaffolding protein MAGI-1 interacts with the Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor (CAR).Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Apr;61:29-34. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.01.012. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25622559 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide methylation patterns in Marfan syndrome.Clin Epigenetics. 2021 Dec 11;13(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s13148-021-01204-4. Clin Epigenetics. 2021. PMID: 34895303 Free PMC article.
-
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and chronic kidney disease in pediatric patients.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2011 Sep;18(5):332-8. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2011.03.005. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2011. PMID: 21896374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutation conferring apical-targeting motif on AE1 exchanger causes autosomal dominant distal RTA.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Jul;23(7):1238-49. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012020112. Epub 2012 Apr 19. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22518001 Free PMC article.
-
A New Story of the Three Magi: Scaffolding Proteins and lncRNA Suppressors of Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 24;13(17):4264. doi: 10.3390/cancers13174264. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34503076 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kitiyakara C., Eggers P., Kopp J. B. (2004) Am. J. Kidney Dis. 44, 815–825 - PubMed
-
- Rydel J. J., Korbet S. M., Borok R. Z., Schwartz M. M. (1995) Am. J. Kidney Dis. 25, 534–542 - PubMed
-
- Korbet S. M., Schwartz M. M., Lewis E. J. (1994) Am. J. Kidney Dis. 23, 773–783 - PubMed
-
- Pollak M. R. (2003) Semin. Nephrol. 23, 141–146 - PubMed
-
- Kestilä M., Lenkkeri U., Männikkö M., Lamerdin J., McCready P., Putaala H., Ruotsalainen V., Morita T., Nissinen M., Herva R., Kashtan C. E., Peltonen L., Holmberg C., Olsen A., Tryggvason K. (1998) Mol. Cell 1, 575–582 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

