Arginine methylation in subunits of mammalian pre-mRNA cleavage factor I
- PMID: 20562214
- PMCID: PMC2905762
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2164210
Arginine methylation in subunits of mammalian pre-mRNA cleavage factor I
Abstract
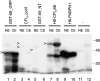
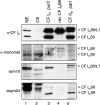
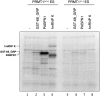
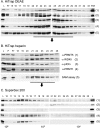
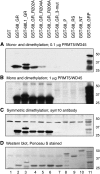
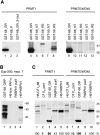
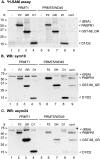
Mammalian cleavage factor I (CF I(m)) is composed of two polypeptides of 25 kDa and either a 59 or 68 kDa subunit (CF I(m)25, CF I(m)59, CF I(m)68). It is part of the cleavage and polyadenylation complex responsible for processing the 3' ends of messenger RNA precursors. To investigate post-translational modifications in factors of the 3' processing complex, we systematically searched for enzymes that modify arginines by the addition of methyl groups. Protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs) are such enzymes that transfer methyl groups from S-adenosyl methionine to arginine residues within polypeptide chains resulting in mono- or dimethylated arginines. We found that CF I(m)68 and the nuclear poly(A) binding protein 1 (PABPN1) were methylated by HeLa cell extracts in vitro. By fractionation of these extracts followed by mass spectral analysis, we could demonstrate that the catalytic subunit PRMT5, together with its cofactor WD45, could symmetrically dimethylate CF I(m)68, whereas pICln, the third polypeptide of the complex, was stimulatory. As sites of methylation in CF I(m)68 we could exclusively identify arginines in a GGRGRGRF or "GAR" motif that is conserved in vertebrates. Further in vitro assays revealed a second methyltransferase, PRMT1, which modifies CF I(m)68 by asymmetric dimethylation of the GAR motif and also weakly methylates the C-termini of both CF I(m)59 and CF I(m)68. The results suggest that native-as compared with recombinant-protein substrates may contain additional determinants for methylation by specific PRMTs. A possible involvement of CF I(m) methylation in the context of RNA export is discussed.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Arginine methylation of a mitochondrial guide RNA binding protein from Trypanosoma brucei.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2001 Nov;118(1):49-59. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(01)00367-x. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2001. PMID: 11704273
-
NF90/NFAR (nuclear factors associated with dsRNA) - a new methylation substrate of the PRMT5-WD45-RioK1 complex.Biol Chem. 2022 Aug 31;403(10):907-915. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2022-0136. Print 2022 Sep 27. Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 36040368
-
Promiscuous modification of the nuclear poly(A)-binding protein by multiple protein-arginine methyltransferases does not affect the aggregation behavior.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jul 18;283(29):20408-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802329200. Epub 2008 May 21. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18495660
-
Methylation of the nuclear poly(A)-binding protein by type I protein arginine methyltransferases - how and why.Biol Chem. 2013 Aug;394(8):1029-43. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2013-0121. Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23412876 Review.
-
Arginine Methylation: The Coming of Age.Mol Cell. 2017 Jan 5;65(1):8-24. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.11.003. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28061334 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative host protein interactions with HTLV-1 p30 and HTLV-2 p28: insights into difference in pathobiology of human retroviruses.Retrovirology. 2012 Aug 9;9:64. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-9-64. Retrovirology. 2012. PMID: 22876852 Free PMC article.
-
Noncanonical Alternative Polyadenylation Contributes to Gene Regulation in Response to Hypoxia.Plant Cell. 2017 Jun;29(6):1262-1277. doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00746. Epub 2017 May 30. Plant Cell. 2017. PMID: 28559476 Free PMC article.
-
Roscovitine inhibits EBNA1 serine 393 phosphorylation, nuclear localization, transcription, and episome maintenance.J Virol. 2011 Mar;85(6):2859-68. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01628-10. Epub 2011 Jan 5. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21209116 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Protein Arginine Methylation in mRNP Dynamics.Mol Biol Int. 2011;2011:163827. doi: 10.4061/2011/163827. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Mol Biol Int. 2011. PMID: 22091396 Free PMC article.
-
The Cleavage and Polyadenylation Specificity Factor 6 (CPSF6) Subunit of the Capsid-recruited Pre-messenger RNA Cleavage Factor I (CFIm) Complex Mediates HIV-1 Integration into Genes.J Biol Chem. 2016 May 27;291(22):11809-19. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.721647. Epub 2016 Mar 18. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26994143 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bedford MT, Richard S 2005. Arginine methylation an emerging regulator of protein function. Mol Cell 18: 263–272 - PubMed
-
- Bedford MT, Frankel A, Yaffe MB, Clarke S, Leder P, Richard S 2000. Arginine methylation inhibits the binding of proline-rich ligands to Src homology 3, but not WW, domains. J Biol Chem 275: 16030–16036 - PubMed
-
- Berger I, Fitzgerald DJ, Richmond TJ 2004. Baculovirus expression system for heterologous multiprotein complexes. Nat Biotechnol 22: 1583–1587 - PubMed
-
- Boisvert FM, Cote J, Boulanger MC, Richard S 2003. A proteomic analysis of arginine-methylated protein complexes. Mol Cell Proteomics 2: 1319–1330 - PubMed
-
- Branscombe TL, Frankel A, Lee JH, Cook JR, Yang Z, Pestka S, Clarke S 2001. PRMT5 (Janus kinase-binding protein 1) catalyzes the formation of symmetric dimethylarginine residues in proteins. J Biol Chem 276: 32971–32976 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
