cPLA2 is protective against COX inhibitor-induced intestinal damage
- PMID: 20562220
- PMCID: PMC2923287
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq184
cPLA2 is protective against COX inhibitor-induced intestinal damage
Abstract
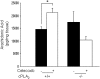
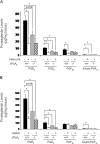
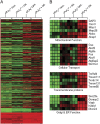
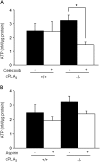
Cytosolic phospholipase A(2) (cPLA(2)) is the rate-limiting enzyme responsible for the generation of prostaglandins (PGs), which are bioactive lipids that play critical roles in maintaining gastrointestinal (GI) homeostasis. There has been a long-standing association between administration of cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitors and GI toxicity. GI injury is thought to be induced by suppressed production of GI-protective PGs as well as direct injury to enterocytes. The present study sought to determine how pan-suppression of PG production via a genetic deletion of cPLA(2) impacts the susceptibility to COX inhibitor-induced GI injury. A panel of COX inhibitors including celecoxib, rofecoxib, sulindac, and aspirin were administered via diet to cPLA(2)(-/-) and cPLA(2)(+/+) littermates. Administration of celecoxib, rofecoxib, and sulindac, but not aspirin, resulted in acute lethality (within 2 weeks) in cPLA(2)(-/-) mice, but not in wild-type littermates. Histomorphological analysis revealed severe GI damage following celecoxib exposure associated with acute bacteremia and sepsis. Intestinal PG levels were reduced equivalently in both genotypes following celecoxib exposure, indicating that PG production was not likely responsible for the differential sensitivity. Gene expression profiling in the small intestines of mice identified drug-related changes among a panel of genes including those involved in mitochondrial function in cPLA(2)(-/-) mice. Further analysis of enterocytic mitochondria showed abnormal morphology as well as impaired ATP production in the intestines from celecoxib-exposed cPLA(2)(-/-) mice. Our data demonstrate that cPLA(2) appears to be an important component in conferring protection against COX inhibitor-induced enteropathy, which may be mediated through affects on enterocytic mitochondria.
Figures




References
-
- Adler DH, Cogan JD, Phillips JA, III, Schnetz-Boutaud N, Milne GL, Iverson T, Stein JA, Brenner DA, Morrow JD, Boutaud O, et al. Inherited human cPLA(2alpha) deficiency is associated with impaired eicosanoid biosynthesis, small intestinal ulceration, and platelet dysfunction. J. Clin. Invest. 2008;118:2121–2131. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bidgood MJ, Jamal OS, Cunningham AM, Brooks PM, Scott KF. Type IIA secretory phospholipase A2 up-regulates cyclooxygenase-2 and amplifies cytokine-mediated prostaglandin production in human rheumatoid synoviocytes. J. Immunol. 2000;165:2790–2797. - PubMed
-
- Bjarnason I, Hayllar J, MacPherson AJ, Russell AS. Side effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the small and large intestine in humans. Gastroenterology. 1993;104:1832–1847. - PubMed
-
- Bombardier C, Laine L, Reicin A, Shapiro D, Burgos-Vargas R, Davis B, Day R, Ferraz MB, Hawkey CJ, Hochberg MC, et al. Comparison of upper gastrointestinal toxicity of rofecoxib and naproxen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. VIGOR Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000;343:1520–1528. 2 p following 1528. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed

