Isolation of VanA-type vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus strains from domestic poultry products with enrichment by incubation in buffered peptone water at 42 degrees C
- PMID: 20562291
- PMCID: PMC2916473
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00071-10
Isolation of VanA-type vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus strains from domestic poultry products with enrichment by incubation in buffered peptone water at 42 degrees C
Abstract
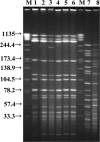
Eight VanA-type enterococcal strains were isolated from 8 of 171 domestic poultry products by using enrichment by incubation in buffered peptone water at 35 degrees C and 42 degrees C. The pulsed-field gel electrophoresis patterns of all six VanA-type Enterococcus faecalis isolates were nearly indistinguishable, indicating the presence of a specific clone in Japan.
Figures
References
-
- Bonten, M. J. M., R. Willems, and R. A. Weinstein. 2001. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci: why are they here, and where do they come from? Lancet Infect. Dis. 1:314-325. - PubMed
-
- Borgen, K., G. S. Simonsen, A. Sundsfjord, Y. Wasteson, Ø. Olsvik, and H. Kruse. 2000. Continuing high prevalence of VanA-type vancomycin-resistant enterococci on Norwegian poultry farms three years after avoparcin was banned. J. Appl. Microbiol. 89:478-485. - PubMed
-
- Borgen, K., M. Sørum, Y. Wasteson, and H. Kruse. 2001. VanA-type vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) remain prevalent in poultry carcasses 3 years after avoparcin was banned. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 64:89-94. - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2009. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 19th informational supplement. CLSI document M100-S19. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

