Platelet-derived growth factor enhances platelet recovery in a murine model of radiation-induced thrombocytopenia and reduces apoptosis in megakaryocytes via its receptors and the PI3-k/Akt pathway
- PMID: 20562316
- PMCID: PMC2948101
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2009.020958
Platelet-derived growth factor enhances platelet recovery in a murine model of radiation-induced thrombocytopenia and reduces apoptosis in megakaryocytes via its receptors and the PI3-k/Akt pathway
Abstract
Background: Platelet-derived growth factor is involved in the regulation of hematopoiesis. Imatinib mesylate, a platelet-derived growth factor receptor inhibitor, induces thrombocytopenia in a significant proportion of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Although our previous studies showed that platelet-derived growth factor enhances megakaryocytopoiesis in vitro, the in vivo effect of platelet-derived growth factor in a model of radiation-induced thrombocytopenia has not been reported.
Design and methods: In this study, we investigated the effect of platelet-derived growth factor on hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells and platelet production using an irradiated-mouse model. We also explored the potential molecular mechanisms of platelet-derived growth factor on thrombopoiesis in M-07e cells.
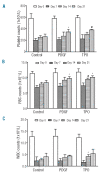
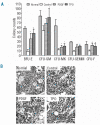
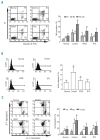
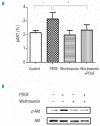
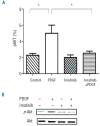
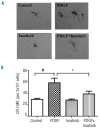
Results: Platelet-derived growth factor, like thrombopoietin, significantly promoted the recovery of platelets and the formation of bone marrow colony-forming unit-megakaryocyte in irradiated mice. Histology confirmed the protective effect of platelet-derived growth factor, as shown by an increased number of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells and a reduction of apoptosis. In a megakaryocytic apoptotic model, platelet-derived growth factor had a similar anti-apoptotic effect as thrombopoietin on megakaryocytes. We also demonstrated that platelet-derived growth factor activated the PI3-k/Akt signaling pathway, while addition of imatinib mesylate reduced p-Akt expression.
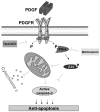
Conclusions: Our findings show that platelet-derived growth factor enhances platelet recovery in mice with radiation-induced thrombocytopenia. This radioprotective effect is likely to be mediated via platelet-derived growth factor receptors with subsequent activation of the PI3-k/Akt pathway. We also provide a possible explanation that blockage of platelet-derived growth factor receptors may reduce thrombopoiesis and play a role in imatinib mesylate-induced thrombocytopenia.
Figures
References
-
- Bergsten E, Uutela M, Li X, Pietras K, Ostman A, Heldin CH, et al. PDGF-D is a specific, protease-activated ligand for the PDGF beta-receptor. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3(5):512–6. - PubMed
-
- Gilbertson DG, Duff ME, West JW, Kelly JD, Sheppard PO, Hofstrand PD, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor C (PDGF-C), a novel growth factor that binds to PDGF alpha and beta receptor. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(29):27406–14. - PubMed
-
- Leveen P, Pekny M, Gebremedhin S, Swolin B, Larsson E, Betsholtz C. Mice deficient for PDGF-B show renal, cardiovascular, and hematological abnormalities. Gene Dev. 1994;8(16):1875–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

