Ion/substrate-dependent conformational dynamics of a bacterial homolog of neurotransmitter:sodium symporters
- PMID: 20562855
- PMCID: PMC3245867
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1854
Ion/substrate-dependent conformational dynamics of a bacterial homolog of neurotransmitter:sodium symporters
Abstract
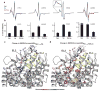
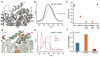
Crystallographic, computational and functional analyses of LeuT have revealed details of the molecular architecture of Na(+)-coupled transporters and the mechanistic nature of ion/substrate coupling, but the conformational changes that support a functional transport cycle have yet to be described fully. We have used site-directed spin labeling and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) analysis to capture the dynamics of LeuT in the region of the extracellular vestibule associated with the binding of Na(+) and leucine. The results outline the Na(+)-dependent formation of a dynamic outward-facing intermediate that exposes the primary substrate binding site and the conformational changes that occlude this binding site upon subsequent binding of the leucine substrate. Furthermore, the binding of the transport inhibitors tryptophan, clomipramine and octyl-glucoside is shown to induce structural changes that distinguish the resulting inhibited conformation from the Na(+)/leucine-bound state.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing financial interests.
Figures





References
-
- Nelson N. The family of Na+/Cl− neurotransmitter transporters. J Neurochem. 1998;71:1785–803. - PubMed
-
- Amara SG, Sonders MS. Neurotransmitter transporters as molecular targets for addictive drugs. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1998;51:87–96. - PubMed
-
- Rudnick G, editor. Mechanisms of biogenic amine neurotransmitter transporters. Humana Press Inc; Totowa, New Jersey: 2002. pp. 25–52.
-
- Krause S, Schwarz W. Identification and selective inhibition of the channel mode of the neuronal GABA transporter 1. Mol Pharmacol. 2005;68:1728–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

