NMR Determination of Protein pK(a) Values in the Solid State
- PMID: 20563223
- PMCID: PMC2885713
- DOI: 10.1021/jz1004413
NMR Determination of Protein pK(a) Values in the Solid State
Abstract
Charged residues play an important role in defining key mechanistic features in many biomolecules. Determining the pK(a) values of large, membrane or fibrillar proteins can be challenging with traditional methods. In this study we show how solid-state NMR is used to monitor chemical shift changes during a pH titration for the small soluble β1 immunoglobulin binding domain of protein G. The chemical shifts of all the amino acids with charged side-chains throughout the uniformly-(13)C,(15)N-labeled protein were monitored over several samples varying in pH; pK(a) values were determined from these shifts for E27, D36, and E42, and the bounds for the pK(a) of other acidic side-chain resonances were determined. Additionally, this study shows how the calculated pK(a) values give insights into the crystal packing of the protein.
Figures
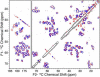
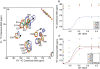
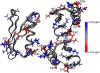
Similar articles
-
Carboxyl pK(a) values, ion pairs, hydrogen bonding, and the pH-dependence of folding the hyperthermophile proteins Sac7d and Sso7d.J Mol Biol. 2007 Sep 28;372(4):992-1008. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.06.089. Epub 2007 Jul 10. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17692336 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of pK(a) values of carboxyl groups in the N-terminal domain of rat CD2: anomalous pK(a) of a glutamate on the ligand-binding surface.Biochemistry. 2000 Jun 13;39(23):6814-24. doi: 10.1021/bi992209z. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10841761
-
Site-Specific Internal Motions in GB1 Protein Microcrystals Revealed by 3D ²H-¹³C-¹³C Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy.J Am Chem Soc. 2016 Mar 30;138(12):4105-19. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b12974. Epub 2016 Mar 18. J Am Chem Soc. 2016. PMID: 26849428 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of mutations of the active site arginine residues in 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase on the pKa values of active site residues and on the pH dependence of catalysis.Biochemistry. 1999 Sep 21;38(38):12358-66. doi: 10.1021/bi9911177. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10493803
-
Interhelical ion pairing in coiled coils: solution structure of a heterodimeric leucine zipper and determination of pKa values of Glu side chains.Biochemistry. 2000 Oct 24;39(42):12804-18. doi: 10.1021/bi001242e. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 11041845
Cited by
-
On the use of ultracentrifugal devices for routine sample preparation in biomolecular magic-angle-spinning NMR.J Biomol NMR. 2017 Mar;67(3):165-178. doi: 10.1007/s10858-017-0089-6. Epub 2017 Feb 22. J Biomol NMR. 2017. PMID: 28229262 Free PMC article.
-
3D Interaction Homology: Computational Titration of Aspartic Acid, Glutamic Acid and Histidine Can Create pH-Tunable Hydropathic Environment Maps.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Nov 3;8:773385. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.773385. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34805282 Free PMC article.
-
Protonation State of an Important Histidine from High Resolution Structures of Lytic Polysaccharide Monooxygenases.Biomolecules. 2022 Jan 24;12(2):194. doi: 10.3390/biom12020194. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204695 Free PMC article.
-
Deuterium-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for Histidine pKa Determination in a pH-Responsive Hydrogel.Biophys J. 2020 Nov 3;119(9):1701-1705. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.09.011. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 33080220 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular pH-response mechanism of the plant light-stress sensor PsbS.Nat Commun. 2021 Apr 16;12(1):2291. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22530-4. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33863895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harris TK, Turner GJ. Structural Basis of Perturbed pKa Values of Catalytic Groups in Enzyme Active Sites. IUBMB Life. 2002;53:85–98. - PubMed
-
- Cleland WW, Kreevoy MM. Low-Barrier Hydrogen-Bonds and Enzymatic Catalysis. Science. 1994;264:1887–1890. - PubMed
-
- McIntosh LP, Hand G, Johnson PE, Joshi MD, Korner M, Plesniak LA, Ziser L, Wakarchuk WW, Withers SG. The pKa of the General Acid/Base Carboxyl Group of a Glycosidase Cycles During Catalysis: A 13C-NMR Study of Bacillus Circuluns Xylanase. Biochemistry. 1996;35:9958–9966. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

