Effect of imaging and catheter characteristics on clinical outcome for patients in the PRECISE study
- PMID: 20563833
- PMCID: PMC2996533
- DOI: 10.1007/s11060-010-0255-0
Effect of imaging and catheter characteristics on clinical outcome for patients in the PRECISE study
Abstract
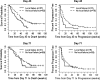
The PRECISE study used convection enhanced delivery (CED) to infuse IL13-PE38QQR in patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) and compared survival to Gliadel Wafers (GW). The objectives of this retrospective evaluation were to assess: (1) catheter positioning in relation to imaging features and (2) to examine the potential impact of catheter positioning, overall catheter placement and imaging features on long term clinical outcome in the PRECISE study. Catheter positioning and overall catheter placement were scored and used as a surrogate of adequate placement. Imaging studies obtained on day 43 and day 71 after resection were each retrospectively reviewed. Catheter positioning scores, catheter overall placement scores, local tumor control and imaging change scores were reviewed and correlated using Generalized Linear Mixed Models. Cox PH regression analysis was used to examine whether these imaging based variables predicted overall survival (OS) and progression free survival (PFS) after adjusting for age and KPS. Of 180 patients in the CED group, 20 patients did not undergo gross total resection. Of the remaining 160 patients only 53% of patients had fully conforming catheters in respect to overall placement and 51% had adequate catheter positioning scores. Better catheter positioning scores were not correlated with local tumor control (P = 0.61) or imaging change score (P = 0.86). OS and PFS were not correlated with catheter positioning score (OS: P = 0.53; PFS: P = 0.72 respectively), overall placement score (OS: P = 0.55; PFS: P = 0.35) or imaging changes on day 43 MRI (P = 0.88). Catheter positioning scores and overall catheter placement scores were not associated with clinical outcome in this large prospective trial.
Figures

References
-
- Stupp R, Dietrich PY, Ostermann Kraljevic S, Pica A, Maillard I, Maeder P, Meuli R, Janzer R, Pizzolato G, Miralbell R, Porchet F, Regli L, de Tribolet N, Mirimanoff RO, Leyvraz S. Promising survival for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme treated with concomitant radiation plus temozolomide followed by adjuvant temozolomide. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:1375–1382. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.5.1375. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sampson JH, Akabani G, Archer GE, Berger MS, Coleman RE, Friedman AH, Friedman HS, Greer K, Herndon JE, 2nd, Kunwar S, McLendon RE, Paolino A, Petry NA, Provenzale JM, Reardon DA, Wong TZ, Zalutsky MR, Pastan I, Bigner DD. Intracerebral infusion of an EGFR-targeted toxin in recurrent malignant brain tumors. Neuro Oncol. 2008;10:320–329. doi: 10.1215/15228517-2008-012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vogelbaum MA, Sampson JH, Kunwar S, Chang SM, Shaffrey M, Asher AL, Lang FF, Croteau D, Parker K, Grahn AY, Sherman JW, Husain SR, Puri RK. Convection-enhanced delivery of cintredekin besudotox (interleukin-13-Pe38qqr) followed by radiation therapy with and without temozolomide in newly diagnosed malignant gliomas: phase 1 study of final safety results. Neurosurgery. 2008;61(5):1031–1037. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000303199.77370.9e. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Debinski W, Obiri NI, Pastan I, Puri RK. A novel chimeric protein composed of interleukin 13 and Pseudomonas exotoxin is highly cytotoxic to human carcinoma cells expressing receptors for interleukin 13 and interleukin 4. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:16775–16780. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.15.8797. - DOI - PubMed

