New outbred colony derived from Mus musculus castaneus to identify skin tumor susceptibility loci
- PMID: 20564342
- PMCID: PMC2892251
- DOI: 10.1002/mc.20635
New outbred colony derived from Mus musculus castaneus to identify skin tumor susceptibility loci
Abstract
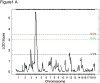
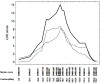
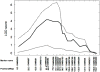
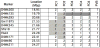
Susceptibility to tumor development varies among mice strains. Using inbred NIH and wild-derived outbred Mus spretus backcrosses, skin cancer-susceptibility loci were mapped [Nagase et al. 1995. Nat Genet 10: 424-429; Nagase et al. 1999. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 15032-15037], and Skts13 was identified as the Aurka gene using a conventional linkage in conjunction with haplotype analysis [Ewart-Toland et al. 2003. Nat Genet 34: 403-412]. In the present study, we examined another wild-derived outbred Mus musculus castaneus in which 10.3% of the analyzed SNPs showed heterogeneity among the colony. All mice examined were completely resistant to the two-stage skin carcinogenesis protocol using 7.12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA)/12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), and this resistant phenotype was dominant when we crossed them with the highly susceptible strain FVB. By scanning F1 backcross progeny between M. m. castaneus and FVB, we found a highly significant linkage for tumor multiplicity on Chromosome 4, which was overlapped with the Skts-fp1 locus, found in the previous study using FVB and PWK cross [Fujiwara et al. 2007. BMC Genet 8: 39]. The linkage was observed in all pedigrees from the five F1 founders, while the linkage for papilloma size on Chromosome 4 was mapped only in pedigrees from founders 1 and 2. By scanning the whole Chromosome 4 of the five F1 founders, founders 1- and 2-specific haplotype block was found between D4Mit293 (20.6 Mbp) and D4Mit171 (22.4 Mbp). In this study we exploited the outbred nature of M. m. castaneus stock to identify a haplotype contributing to papilloma size on mouse Chromosome 4. These data illustrate the strength of using outbred mice in identification of the genetic component of a mouse complex trait such as the skin cancer-susceptibility phenotype.
Figures

References
-
- Nagase H, Bryson S, Cordell H, Kemp CJ, Fee F, Balmain A. Distinct genetic loci control development of benign and malignant skin tumours in mice. Nat Genet. 1995;10:424–429. - PubMed
-
- Ewart-Toland A, Briassouli P, de Koning JP, Mao JH, Yuan J, Chan F, MacCarthy-Morrogh L, Ponder BA, Nagase H, Burn J, Ball S, Almeida M, Linardopoulos S, Balmain A. Identification of Stk6/STK15 as a candidate low-penetrance tumor-susceptibility gene in mouse and human. Nat Genet. 2003;34:403–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

