Biochemical and structural characterization of a ureidoglycine aminotransferase in the Klebsiella pneumoniae uric acid catabolic pathway
- PMID: 20565126
- PMCID: PMC2912414
- DOI: 10.1021/bi1006755
Biochemical and structural characterization of a ureidoglycine aminotransferase in the Klebsiella pneumoniae uric acid catabolic pathway
Abstract
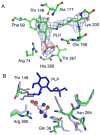
Many plants, fungi, and bacteria catabolize allantoin as a mechanism for nitrogen assimilation. Recent reports have shown that in plants and some bacteria the product of hydrolysis of allantoin by allantoinase is the unstable intermediate ureidoglycine. While this molecule can spontaneously decay, genetic analysis of some bacterial genomes indicates that an aminotransferase may be present in the pathway. Here we present evidence that Klebsiella pneumoniae HpxJ is an aminotransferase that preferentially converts ureidoglycine and an alpha-keto acid into oxalurate and the corresponding amino acid. We determined the crystal structure of HpxJ, allowing us to present an explanation for substrate specificity.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

