Contingency management for cocaine use in methadone maintenance patients: when does abstinence happen?
- PMID: 20565154
- PMCID: PMC2891572
- DOI: 10.1037/a0017542
Contingency management for cocaine use in methadone maintenance patients: when does abstinence happen?
Abstract
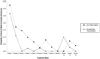
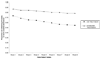
Contingency management (CM) is an efficacious intervention for cocaine abusing methadone patients, but typically only about half of patients respond. By investigating time to onset of cocaine abstinence and factors associated with abstinence, we may be able to more efficiently direct CM approaches to patients most likely to benefit. Onset of cocaine abstinence was evaluated in cocaine abusing methadone maintenance patients (N = 193) enrolled in one of three randomized clinical trials of CM. Participants received standard treatment with frequent urine toxicology monitoring or standard treatment plus CM during the trials. Slightly more than half the sample obtained at least 1 week of cocaine abstinence, and approximately a third of the sample obtained at least 4 weeks of cocaine abstinence. Discrete-time survival and hazard analyses found Weeks 1 and 2 of the intervention period had the greatest probability for the initiation of abstinence, and few participants initiated any period of abstinence after Week 4. Patients randomized to CM, those with more years of cocaine use, and those with less recent cocaine use were more likely to achieve abstinence. Overall, these results indicate onset of cocaine abstinence is likely to occur early in treatment and in individuals with less severe cocaine use. Practical implications of these results for designing and implementing CM interventions in methadone maintenance clinics are discussed.
(PsycINFO Database Record (c) 2010 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures


Similar articles
-
The brief abstinence test: voucher-based reinforcement of cocaine abstinence.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2000 Feb 1;58(1-2):205-12. doi: 10.1016/s0376-8716(99)00090-3. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2000. PMID: 10669073
-
Comparable efficacy of contingency management for cocaine dependence among African American, Hispanic, and White methadone maintenance clients.Psychol Addict Behav. 2009 Mar;23(1):168-74. doi: 10.1037/a0014575. Psychol Addict Behav. 2009. PMID: 19290703 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Methadone versus buprenorphine with contingency management or performance feedback for cocaine and opioid dependence.Am J Psychiatry. 2005 Feb;162(2):340-9. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.162.2.340. Am J Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 15677600 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of opiate maintenance therapy and adjunctive interventions for opioid dependence with comorbid cocaine use disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials.Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2009;35(5):339-49. doi: 10.1080/00952990903108215. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2009. PMID: 20180662
-
Cocaine abuse among methadone maintenance patients: are there effective treatment strategies?J Psychoactive Drugs. 1994 Apr-Jun;26(2):129-36. doi: 10.1080/02791072.1994.10472260. J Psychoactive Drugs. 1994. PMID: 7931857 Review.
Cited by
-
Initiation of abstinence in adolescents treated for marijuana use disorders.J Subst Abuse Treat. 2013 Apr;44(4):384-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2012.08.223. Epub 2012 Oct 22. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2013. PMID: 23085041 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The impact of engagement in street-based income generation activities on stimulant drug use cessation among people who inject drugs.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014 Aug 1;141:58-64. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.05.003. Epub 2014 May 17. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014. PMID: 24909853 Free PMC article.
-
A two-week pilot study of intranasal oxytocin for cocaine-dependent individuals receiving methadone maintenance treatment for opioid use disorder.Addict Res Theory. 2016;24(6):490-498. doi: 10.3109/16066359.2016.1173682. Epub 2016 May 25. Addict Res Theory. 2016. PMID: 28503120 Free PMC article.
-
Placebo-group responders in methamphetamine pharmacotherapy trials: the role of immediate establishment of abstinence.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012 Oct;20(5):430-5. doi: 10.1037/a0029210. Epub 2012 Aug 6. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22867036 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Standard magnitude prize reinforcers can be as efficacious as larger magnitude reinforcers in cocaine-dependent methadone patients.J Consult Clin Psychol. 2015 Jun;83(3):464-72. doi: 10.1037/a0037888. Epub 2014 Sep 8. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2015. PMID: 25198284 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Dallery J, Silverman K, Chutuape M, Bigelow G, Stitzer M. Voucher-based reinforcement of opiate plus cocaine abstinence in treatment-resistant methadone patients: Effects of reinforce magnitude. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2001;9:317–325. - PubMed
-
- DeMaria PA, Sterling R, Weinstein SP. The effect of stimulant and sedative use on treatment outcome of patients admitted to methadone maintenance treatment. American Journal on Addictions. 2000;9:145–153. - PubMed
-
- Downey KK, Helmus TC, Schuster CR. Treatment of heroin-dependent polydrug abusers with contingency management and buprenorphine maintenance. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2000;8:176–184. - PubMed
-
- Dunteman GH, Condelli WS, Fairbank JA. Predicting cocaine use among methadone patients: Analysis of findings from a national study. Hospital & Community Psychiatry. 1992;43:608–611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DA013444/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32-AA07290/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA024667/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009241/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA024667/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA016855/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA022739/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AA003510/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA016855/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA13444/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA027615/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA003510/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DA023918/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA014618/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA022739/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR06192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AA007290/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA018883/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50-AA03510/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA14618/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA18883/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DA023918/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50-DA09241/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States

