Intracellular Casp8p41 content is inversely associated with CD4 T cell count
- PMID: 20565257
- PMCID: PMC2906377
- DOI: 10.1086/653705
Intracellular Casp8p41 content is inversely associated with CD4 T cell count
Abstract
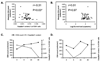
Casp8p41 is a protein fragment generated by cleavage of procaspase 8 by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) protease. We measured Casp8p41 content in memory CD4 T cells and analyzed the association of Casp8p41 content with CD4 T cell count, cross-sectionally and longitudinally. Casp8p41 content was inversely correlated with CD4 T cell count, and change in Casp8p41 content was associated with absolute CD4 T cell count with change over time. Casp8p41 change was a better predictor of CD4 T cell count change than activated CD8 T cell percentage or viral load and was comparable to bacterial 16s DNA levels. This suggests that Casp8p41 is a relevant mediator of CD4 T cell death during HIV infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest: A patent for Casp8p41 has been filed by Dr Andrew Badley. The remaining authors report that they do not have a commercial or other association that might pose a conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pandolfi F, Pierdominici M, Oliva A, et al. Apoptosis-related mortality in vitro of mononuclear cells from patients with HIV infection correlates with disease severity and progression. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995;9:450–458. - PubMed
-
- Gougeon ML, Lecoeur H, Dulioust A, et al. Programmed cell death in peripheral lymphocytes from HIV-infected persons: increased susceptibility to apoptosis of CD4 and CD8 T cells correlates with lymphocyte activation and with disease progression. J Immunol. 1996;156:3509–3520. - PubMed
-
- Samuelsson A, Brostrom C, van Dijk N, Sonnerborg A, Chiodi F. Apoptosis of CD4+ and CD19+ cells during human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection–correlation with clinical progression, viral load, and loss of humoral immunity. Virology. 1997;238:180–188. - PubMed
-
- Rothen M, Gratzl S, Hirsch HH, Moroni C. Apoptosis in HIV-infected individuals is an early marker occurring independently of high viremia. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1997;13:771–779. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI62261/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 69501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI062261/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI069994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI40384/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH59037/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007013/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI069994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH059037/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 A127763/PHS HHS/United States
- P30 AI27763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI040384/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI040384/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

