Modelling crack cocaine use trends over 10 years in a Canadian setting
- PMID: 20565519
- PMCID: PMC4643832
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1465-3362.2009.00145.x
Modelling crack cocaine use trends over 10 years in a Canadian setting
Abstract
Introduction and aims: Crack cocaine use among illicit drug users is associated with a range of health and community harms. However, long-term epidemiological data documenting patterns and risk factors for crack use initiation remain limited especially among injection drug users. We investigated longitudinal patterns of crack cocaine use among polydrug users in Vancouver, Canada.
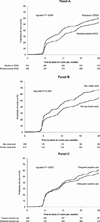
Design and methods: We examined the rate of crack use among injection drug users enrolled in a prospective cohort study in Vancouver, Canada between 1996 and 2005. We also used a Cox proportional hazards regression analysis to identify independent predictors of crack use initiation among this population.
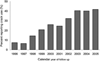
Results: In total, 1603 injection drug users were recruited between May 1996 and December 2005. At baseline, 7.4% of participants reported ever using crack and this rate increased to 42.6% by the end of the study period (Mantel trend test P < 0.001). Independent predictors of crack use initiation during the study period included frequent cocaine injection, crystal methamphetamine injection, residency in the city's drug using epicenter and involvement in the sex trade (all P < 0.05).
Discussion and conclusions: These findings demonstrate a massive increase in crack use among injection drug users in a Canadian setting. Our findings also highlight the complex interactions that contribute to the initiation of crack use among injection drug users and suggest that evidence-based interventions are urgently needed to address crack use initiation and to address harms associated with its ongoing use.
Conflict of interest statement
D. W., K. D., T. K., K. L. and E. W. have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- UNODC. World Drug Report 2007. Report. Vienna: United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime; 2007.
-
- Faruque S, Edlin BR, McCoy CB, et al. Crack cocaine smoking and oral sores in three inner-city neighborhoods. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1996;13:87. - PubMed
-
- Elifson KW, Boles J, Darrow WW, Sterk CE. HIV seroprevalence and risk factors among clients of female and male prostitutes. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1999;20:195. - PubMed
-
- Doherty MC, Garfein RS, Monterroso E, Brown D, Vlahov D. Correlates of HIV infection among young adult shortterm injection drug users. AIDS. 2000;14:717. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

