Development and evaluation of an open source Delphi-based software for morphometric quantification of liver fibrosis
- PMID: 20565730
- PMCID: PMC2903497
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-1536-3-10
Development and evaluation of an open source Delphi-based software for morphometric quantification of liver fibrosis
Abstract
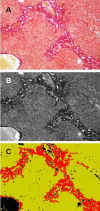
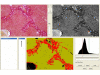
Background: Computer-based morphometry can minimize subjectivity in the assessment of liver fibrosis. An image processing program was developed with Delphi for the quantification of fibrosis in liver tissue samples stained with Sirius Red. Bile duct ligated and sham operated wild type C57BL/6 mice served as a model of time-dependent induction of liver fibrosis. Formation of fibrosis was determined with the developed software at day 0, 3, 7, 10, 14, 20, 30 and 60. The results were compared to a semi-quantitative scoring system.
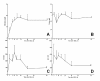
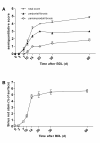
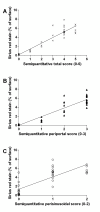
Results: Quantitative accumulation of collagen fibres was observed from day 3 to day 14, with a slight further increase thereafter. During ongoing fibrogenesis, there was a significant elevation of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST) and bilirubin. The results from our computer-based morphometric analysis were highly correlated with the results that were obtained in a standardized pathology semi-quantitative scoring system (R 2 = 0.89, n = 38).
Conclusions: Using our Delphi-based image analysing software, the morphometric assessment of fibrosis is as precise as semi-quantitative scoring by an experienced pathologist. This program can be a valuable tool in any kind of experimental or clinical setting for standardized quantitative assessment of fibrosis.
Figures

References
-
- Portmann BC, Nakanuma Y, editor. Diseases of the Bile Ducts. 5. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 2007.
-
- Caballero T, Perez-Milena A, Masseroli M, O'Valle F, Salmeron FJ, Del Moral RM, Sanchez-Salgado G. Liver fibrosis assessment with semiquantitative indexes and image analysis quantification in sustained-responder and non-responder interferon-treated patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2001;34:740–747. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8278(01)00006-X. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

