Integrin expression profiling identifies integrin alpha5 and beta1 as prognostic factors in early stage non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 20565758
- PMCID: PMC2895598
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-152
Integrin expression profiling identifies integrin alpha5 and beta1 as prognostic factors in early stage non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Selection of early stage non-small cell lung cancer patients with a high risk of recurrence is warranted in order to select patients who will benefit from adjuvant treatment strategies. We evaluated the prognostic value of integrin expression profiles in a retrospective study on frozen primary tumors of 68 patients with early stage non-small cell lung cancer.
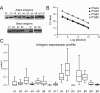
Methods: A retrospective study was performed on frozen primary tumors of 68 early stage non-small cell lung cancer patients with a follow up of at least 10 years. From all tumor tissues, RNA was isolated and reverse transcribed into cDNA. qPCR was used to generate mRNA expression profiles including integrins alpha1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 11, and V as well as integrins beta1, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8.
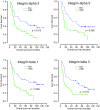
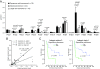
Results: The expression levels of integrins alpha5, beta1 and beta3 predicted overall survival and disease free survival in early stage NSCLC patients. There was no association between integrin expression and lymph node metastases. Comparison between the histological subtypes revealed a distinct integrin signature for squamous cell carcinoma while the profiles of adenocarcinoma and large cell carcinoma were largely the same.
Conclusion: Integrin expression in NSCLC is important for the development and behavior of the tumor and influences the survival of the patient. Determining the integrin expression profile might serve as a tool in predicting the prognosis of individual patients.
Figures

Similar articles
-
AlphaV- and beta1-integrin subunits are commonly expressed in malignant effusions from ovarian carcinoma patients.Gynecol Oncol. 2003 Aug;90(2):248-57. doi: 10.1016/s0090-8258(03)00321-4. Gynecol Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12893184
-
Prognostic value of β1 integrin expression in colorectal liver metastases.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013 Dec 15;7(1):288-300. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013. PMID: 24427350 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced integrin alpha3 expression as a factor of poor prognosis of patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung.J Clin Oncol. 1998 Mar;16(3):1060-7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1998.16.3.1060. J Clin Oncol. 1998. PMID: 9508191
-
Prognostic value of ERCC1, RRM1, BRCA1 and SETDB1 in early stage of non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2016 Aug;18(8):798-804. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1440-6. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Clin Transl Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26542178
-
Prognostic value of ERCC1 mRNA expression in non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, and gastric cancer in patients from Southern China.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Dec 1;7(12):8312-21. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25674197 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Small breast epithelial mucin tumor tissue expression is associated with increased risk of recurrence and death in triple-negative breast cancer patients.Diagn Pathol. 2013 May 1;8:71. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-8-71. Diagn Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23635316 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced Graphene Oxide Modulates the FAK-Dependent Signaling Pathway in Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells In Vitro.Materials (Basel). 2022 Aug 24;15(17):5843. doi: 10.3390/ma15175843. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36079225 Free PMC article.
-
Sepsis lethality via exacerbated tissue infiltration and TLR-induced cytokine production by neutrophils is integrin α3β1-dependent.Blood. 2014 Dec 4;124(24):3515-23. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-01-552943. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Blood. 2014. PMID: 25278585 Free PMC article.
-
α5β1-Integrin promotes tension-dependent mammary epithelial cell invasion by engaging the fibronectin synergy site.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Nov 1;28(22):2958-2977. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-02-0126. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28877984 Free PMC article.
-
Zoledronate blocks geranylgeranylation not farnesylation to suppress human osteosarcoma U2OS cells metastasis by EMT via Rho A activation and FAK-inhibited JNK and p38 pathways.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 1;7(9):9742-58. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7138. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26848867 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

