Promoter- and cell-specific epigenetic regulation of CD44, Cyclin D2, GLIPR1 and PTEN by methyl-CpG binding proteins and histone modifications
- PMID: 20565761
- PMCID: PMC2912262
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-297
Promoter- and cell-specific epigenetic regulation of CD44, Cyclin D2, GLIPR1 and PTEN by methyl-CpG binding proteins and histone modifications
Abstract
Background: The aim of the current study was to analyze the involvement of methyl-CpG binding proteins (MBDs) and histone modifications on the regulation of CD44, Cyclin D2, GLIPR1 and PTEN in different cellular contexts such as the prostate cancer cells DU145 and LNCaP, and the breast cancer cells MCF-7. Since global chromatin changes have been shown to occur in tumours and regions of tumour-associated genes are affected by epigenetic modifications, these may constitute important regulatory mechanisms for the pathogenesis of malignant transformation.
Methods: In DU145, LNCaP and MCF-7 cells mRNA expression levels of CD44, Cyclin D2, GLIPR1 and PTEN were determined by quantitative RT-PCR at the basal status as well as after treatment with demethylating agent 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine and/or histone deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A. Furthermore, genomic DNA was bisulfite-converted and sequenced. Chromatin immunoprecipitation was performed with the stimulated and unstimulated cells using antibodies for MBD1, MBD2 and MeCP2 as well as 17 different histone antibodies.
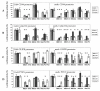
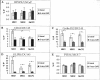
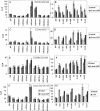
Results: Comparison of the different promoters showed that MeCP2 and MBD2a repressed promoter-specifically Cyclin D2 in all cell lines, whereas in MCF-7 cells MeCP2 repressed cell-specifically all methylated promoters. Chromatin immunoprecipitation showed that all methylated promoters associated with at least one MBD. Treatment of the cells by the demethylating agent 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine (5-aza-CdR) caused dissociation of the MBDs from the promoters. Only MBD1v1 bound and repressed methylation-independently all promoters. Real-time amplification of DNA immunoprecipitated by 17 different antibodies showed a preferential enrichment for methylated lysine of histone H3 (H3K4me1, H3K4me2 and H3K4me3) at the particular promoters. Notably, the silent promoters were associated with unmodified histones which were acetylated following treatment by 5-aza-CdR.
Conclusions: This study is one of the first to reveal the histone code and MBD profile at the promoters of CD44, Cyclin D2, GLIPR1 and PTEN in different tumour cells and associated changes after stimulation with methylation inhibitor 5-aza-CdR.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Selective association of the methyl-CpG binding protein MBD2 with the silent p14/p16 locus in human neoplasia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Apr 24;98(9):4990-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.101617298. Epub 2001 Apr 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11309512 Free PMC article.
-
hMLH1 promoter methylation and silencing in primary endometrial cancers are associated with specific alterations in MBDs occupancy and histone modifications.Gynecol Oncol. 2006 Oct;103(1):321-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2006.03.045. Epub 2006 May 15. Gynecol Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16701802 Free PMC article.
-
CpG island promoter methylation and silencing of 14-3-3sigma gene expression in LNCaP and Tramp-C1 prostate cancer cell lines is associated with methyl-CpG-binding protein MBD2.Oncogene. 2006 Aug 3;25(33):4559-72. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209462. Epub 2006 Jun 19. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16786000 Free PMC article.
-
Gene methylation in gastric cancer.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 May 10. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23669186 Review.
-
What Do We Have to Know about PD-L1 Expression in Prostate Cancer? A Systematic Literature Review. Part 5: Epigenetic Regulation of PD-L1.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 15;22(22):12314. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212314. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830196 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic CpG demethylation of the promoter and reactivation of the expression of Neurog1 by curcumin in prostate LNCaP cells.AAPS J. 2011 Dec;13(4):606-14. doi: 10.1208/s12248-011-9300-y. Epub 2011 Sep 22. AAPS J. 2011. PMID: 21938566 Free PMC article.
-
Natural compound-derived epigenetic regulators targeting epigenetic readers, writers and erasers.Curr Top Med Chem. 2016;16(7):697-713. doi: 10.2174/1568026615666150826114359. Curr Top Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26306989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA methylation of claudin-6 promotes breast cancer cell migration and invasion by recruiting MeCP2 and deacetylating H3Ac and H4Ac.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 26;35(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0396-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27461117 Free PMC article.
-
CAP superfamily proteins in human: a new target for cancer therapy.Med Oncol. 2024 Nov 5;41(12):306. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02548-6. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39499355 Review.
-
The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: therapeutic implications.J Hematol Oncol. 2018 May 10;11(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0605-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29747682 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

