Comparison and calibration of transcriptome data from RNA-Seq and tiling arrays
- PMID: 20565764
- PMCID: PMC3091629
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-383
Comparison and calibration of transcriptome data from RNA-Seq and tiling arrays
Abstract
Background: Tiling arrays have been the tool of choice for probing an organism's transcriptome without prior assumptions about the transcribed regions, but RNA-Seq is becoming a viable alternative as the costs of sequencing continue to decrease. Understanding the relative merits of these technologies will help researchers select the appropriate technology for their needs.
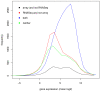
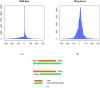
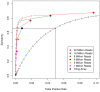
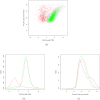
Results: Here, we compare these two platforms using a matched sample of poly(A)-enriched RNA isolated from the second larval stage of C. elegans. We find that the raw signals from these two technologies are reasonably well correlated but that RNA-Seq outperforms tiling arrays in several respects, notably in exon boundary detection and dynamic range of expression. By exploring the accuracy of sequencing as a function of depth of coverage, we found that about 4 million reads are required to match the sensitivity of two tiling array replicates. The effects of cross-hybridization were analyzed using a "nearest neighbor" classifier applied to array probes; we describe a method for determining potential "black list" regions whose signals are unreliable. Finally, we propose a strategy for using RNA-Seq data as a gold standard set to calibrate tiling array data. All tiling array and RNA-Seq data sets have been submitted to the modENCODE Data Coordinating Center.
Conclusions: Tiling arrays effectively detect transcript expression levels at a low cost for many species while RNA-Seq provides greater accuracy in several regards. Researchers will need to carefully select the technology appropriate to the biological investigations they are undertaking. It will also be important to reconsider a comparison such as ours as sequencing technologies continue to evolve.
Figures



References
-
- Kapranov P, Cawley SE, Drenkow J, Bekiranov S, Strausberg RL, Fodor SPA, Gingeras TR. Large-scale transcriptional activity in chromosomes 21 and 22. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2002;296(5569):916–919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

