Population based allele frequencies of disease associated polymorphisms in the Personalized Medicine Research Project
- PMID: 20565774
- PMCID: PMC2908055
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2156-11-51
Population based allele frequencies of disease associated polymorphisms in the Personalized Medicine Research Project
Abstract
Background: There is a lack of knowledge regarding the frequency of disease associated polymorphisms in populations and population attributable risk for many populations remains unknown. Factors that could affect the association of the allele with disease, either positively or negatively, such as race, ethnicity, and gender, may not be possible to determine without population based allele frequencies.Here we used a panel of 51 polymorphisms previously associated with at least one disease and determined the allele frequencies within the entire Personalized Medicine Research Project population based cohort. We compared these allele frequencies to those in dbSNP and other data sources stratified by race. Differences in allele frequencies between self reported race, region of origin, and sex were determined.
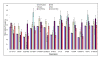
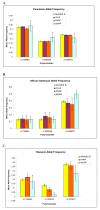
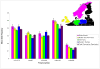
Results: There were 19544 individuals who self reported a single racial category, 19027 or (97.4%) self reported white Caucasian, and 11205 (57.3%) individuals were female. Of the 11,208 (57%) individuals with an identifiable region of origin 8337 or (74.4%) were German.41 polymorphisms were significantly different between self reported race at the 0.05 level. Stratification of our Caucasian population by self reported region of origin revealed 19 polymorphisms that were significantly different (p = 0.05) between individuals of different origins. Further stratification of the population by gender revealed few significant differences in allele frequencies between the genders.
Conclusions: This represents one of the largest population based allele frequency studies to date. Stratification by self reported race and region of origin revealed wide differences in allele frequencies not only by race but also by region of origin within a single racial group. We report allele frequencies for our Asian/Hmong and American Indian populations; these two minority groups are not typically selected for population allele frequency detection. Population wide allele frequencies are important for the design and implementation of studies and for determining the relevance of a disease associated polymorphism for a given population.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Frequency of eNOS polymorphisms in the Colombian general population.BMC Genet. 2010 Jun 20;11:54. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-11-54. BMC Genet. 2010. PMID: 20565909 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E polymorphism in Southern Iran: E4 allele in the lowest reported amounts.Mol Biol Rep. 2008 Dec;35(4):495-9. doi: 10.1007/s11033-007-9113-3. Epub 2007 Jun 27. Mol Biol Rep. 2008. PMID: 17594534
-
High allele frequency of CYP2C9*3 (rs1057910) in a Negrito's subtribe population in Malaysia; Aboriginal people of Jahai.Ann Hum Biol. 2016 Sep;43(5):445-50. doi: 10.3109/03014460.2015.1068372. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Ann Hum Biol. 2016. PMID: 26402341
-
Interethnic and intraethnic variability of CYP2C8 and CYP2C9 polymorphisms in healthy individuals.Mol Diagn Ther. 2006;10(1):29-40. doi: 10.1007/BF03256440. Mol Diagn Ther. 2006. PMID: 16646575 Review.
-
Geographic diversity in genotype frequencies and meta-analysis of the association between rs1801282 polymorphisms and gestational diabetes mellitus.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018 Sep;143:15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.05.050. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018. PMID: 29885389 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene-Environment Interactions in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy.Front Neurol. 2021 Apr 9;12:664796. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.664796. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33897612 Free PMC article.
-
Association of TGFB1 rs1800469 and BCMO1 rs6564851 with coronary heart disease and IL1B rs16944 with all-cause mortality in men from the Northern Ireland PRIME study.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 22;17(8):e0273333. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273333. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35994463 Free PMC article.
-
SNPs previously associated with Dupuytren's disease replicated in a North American cohort.Clin Med Res. 2014 Dec;12(3-4):133-7. doi: 10.3121/cmr.2013.1199. Epub 2014 Feb 26. Clin Med Res. 2014. PMID: 24573701 Free PMC article.
-
No association of AQP4 polymorphisms with neuromyelitis optica and multiple sclerosis.Transl Neurosci. 2016 Aug 22;7(1):76-83. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2016-0012. eCollection 2016. Transl Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 28123825 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of 3'UTR genetic variants in PCSK9 and LDLR genes on plasma lipid traits and response to atorvastatin in Brazilian subjects: a pilot study.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Apr 15;8(4):5978-88. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26131194 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

