Whole exome capture in solution with 3 Gbp of data
- PMID: 20565776
- PMCID: PMC2911110
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-6-r62
Whole exome capture in solution with 3 Gbp of data
Abstract
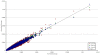
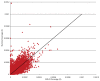
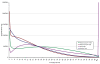
We have developed a solution-based method for targeted DNA capture-sequencing that is directed to the complete human exome. Using this approach allows the discovery of greater than 95% of all expected heterozygous singe base variants, requires as little as 3 Gbp of raw sequence data and constitutes an effective tool for identifying rare coding alleles in large scale genomic studies.
Figures
References
-
- Gnirke A, Melnikov A, Maguire J, Rogov P, LeProust EM, Brockman W, Fennell T, Giannoukos G, Fisher S, Russ C, Gabriel S, Jaffe DB, Lander ES, Nusbaum C. Solution hybrid selection with ultra-long oligonucleotides for massively parallel targeted sequencing. Nat Biotechnol. 2009;27:182–189. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1523. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

