Differences in the BAL proteome after Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in wild type and SP-A-/- mice
- PMID: 20565803
- PMCID: PMC2911411
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-5956-8-34
Differences in the BAL proteome after Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in wild type and SP-A-/- mice
Abstract
Background: Surfactant protein-A (SP-A) has been shown to play a variety of roles related to lung host defense function. Mice lacking SP-A are more susceptible to infection than wild type C57BL/6 mice. We studied bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) protein expression in wild type and SP-A-/- mice infected with Klebsiella pneumoniae by 2D-DIGE.
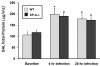
Methods: Mice were infected intratracheally with K. pneumoniae and after 4 and 24 hours they were subject to BAL. Cell-free BAL was analyzed by 2D-DIGE on two-dimensional gels with pH ranges of 4-7 and 7-11. Under baseline conditions and at 4 and 24 hr post-infection BAL was compared between untreated and infected wild type and SP-A-/- mice. Sixty proteins identified by mass spectrometry were categorized as host defense, redox regulation, and protein metabolism/modification.
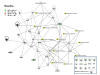
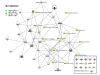
Results: We found: 1) ~75% of 32 host defense proteins were lower in uninfected SP-A-/- vs wild type, suggesting increased susceptibility to infection or oxidative injury; 2) At 4 hr post-infection > 2/3 of identified proteins were higher in SP-A-/- than wild type mice, almost the exact opposite of untreated mice; 3) At 24 hr post-infection some proteins continued increasing, but many returned to baseline; 4) In infected wild type mice significant changes occurred in 13 of 60 proteins, with 12 of 13 increasing, vs on 4 significant changes in SP-A-/- mice. Infection response patterns between strains demonstrated both commonalities and differences. In several cases changes between 4 and 24 hr followed different patterns between strains.
Conclusions: These indicate that SP-A plays a key role in regulating the BAL proteome, functioning indirectly to regulate lung host defense function, possibly via the macrophage. In the absence of SP-A baseline levels of many host defense molecules are lower. However, many of these indirect deficits in SP-A-/- mice are rapidly compensated for during infection, indicating that SP-A also has a direct role on host defense against K. pneumoniae that may be instrumental in determining clinical course.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential Effects of Human SP-A1 and SP-A2 on the BAL Proteome and Signaling Pathways in Response to Klebsiella pneumoniae and Ozone Exposure.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 26;10:561. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00561. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30972061 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of surfactant protein-A on ozone-induced changes in the mouse bronchoalveolar lavage proteome.Proteome Sci. 2009 Mar 26;7:12. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-7-12. Proteome Sci. 2009. PMID: 19323824 Free PMC article.
-
Survival of Surfactant Protein-A1 and SP-A2 Transgenic Mice After Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection, Exhibits Sex-, Gene-, and Variant Specific Differences; Treatment With Surfactant Protein Improves Survival.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 16;9:2404. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02404. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30459763 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo rescue of alveolar macrophages from SP-A knockout mice with exogenous SP-A nearly restores a wild type intracellular proteome; actin involvement.Proteome Sci. 2011 Oct 28;9:67. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-9-67. Proteome Sci. 2011. PMID: 22035134 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of SP-A has a negative impact on the susceptibility of mice to Klebsiella pneumoniae infection after ozone exposure: sex differences.Respir Res. 2008 Dec 4;9(1):77. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-9-77. Respir Res. 2008. PMID: 19055785 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sex differences in the acute in vivo effects of different human SP-A variants on the mouse alveolar macrophage proteome.J Proteomics. 2014 Aug 28;108:427-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2014.06.007. Epub 2014 Jun 18. J Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24954098 Free PMC article.
-
Surfactant protein A is defective in abrogating inflammation in asthma.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011 Oct;301(4):L598-606. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00381.2010. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21784968 Free PMC article.
-
Human Surfactant Protein SP-A1 and SP-A2 Variants Differentially Affect the Alveolar Microenvironment, Surfactant Structure, Regulation and Function of the Alveolar Macrophage, and Animal and Human Survival Under Various Conditions.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 17;12:681639. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.681639. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34484180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Effects of Human SP-A1 and SP-A2 on the BAL Proteome and Signaling Pathways in Response to Klebsiella pneumoniae and Ozone Exposure.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 26;10:561. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00561. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30972061 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of Peroxiredoxin 6 by the Pla Protease of Yersinia pestis.Infect Immun. 2015 Nov 9;84(1):365-74. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01168-15. Print 2016 Jan. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26553463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crouch EC. Collectins and pulmonary host defense. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998;19:177–201. - PubMed
-
- Kremlev SG, Phelps DS. Effect of SP-A and surfactant lipids on expression of cell surface markers in the THP-1 monocytic cell line. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:L1070–L1077. - PubMed
-
- Kremlev SG, Umstead TM, Phelps DS. Surfactant protein A regulates cytokine production in the monocytic cell line THP-1. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:L996–1004. - PubMed
-
- Brinker KG, Garner H, Wright JR. Surfactant protein A modulates the differentiation of murine bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003;284:L232–L241. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

