Expression of growth factor receptors and targeting of EGFR in cholangiocarcinoma cell lines
- PMID: 20565817
- PMCID: PMC2896958
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-302
Expression of growth factor receptors and targeting of EGFR in cholangiocarcinoma cell lines
Abstract
Background: Cholangiocarcinoma (CC) is a malignant neoplasm of the bile ducts or the gallbladder. Targeting of growth factor receptors showed therapeutic potential in palliative settings for many solid tumors. The aim of this study was to determine the expression of seven growth factor receptors in CC cell lines and to assess the effect of blocking the EGFR receptor in vitro.
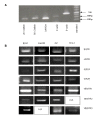
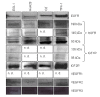
Methods: Expression of EGFR (epithelial growth factor receptor), HGFR (hepatocyte growth factor receptor) IGF1R (insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor), IGF2R (insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor) and VEGFR1-3 (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1-3) were examined in four human CC cell lines (EGI-1, HuH28, OZ and TFK-1). The effect of the anti-EGFR-antibody cetuximab on cell growth and apoptosis was studied and cell lines were examined for KRAS mutations.
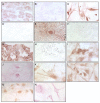
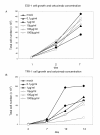
Results: EGFR, HGFR and IGFR1 were present in all four cell lines tested. IGFR2 expression was confirmed in EGI-1 and TFK-1. No growth-inhibitory effect was found in EGI-1 cells after incubation with cetuximab. Cetuximab dose-dependently inhibited growth in TFK-1. Increased apoptosis was only seen in TFK-1 cells at the highest cetuximab dose tested (1 mg/ml), with no dose-response-relationship at lower concentrations. In EGI-1 a heterozygous KRAS mutation was found in codon 12 (c.35G>A; p.G12D). HuH28, OZ and TFK-1 lacked KRAS mutation.
Conclusion: CC cell lines express a pattern of different growth receptors in vitro. Growth factor inhibitor treatment could be affected from the KRAS genotype in CC. The expression of EGFR itself does not allow prognoses on growth inhibition by cetuximab.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genomic and genetic characterization of cholangiocarcinoma identifies therapeutic targets for tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Gastroenterology. 2012 Apr;142(4):1021-1031.e15. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.005. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Gastroenterology. 2012. PMID: 22178589 Free PMC article.
-
Dasatinib sensitizes KRAS mutant colorectal tumors to cetuximab.Oncogene. 2011 Feb 3;30(5):561-74. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.430. Epub 2010 Oct 18. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 20956938 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of the predictive markers amphiregulin and epiregulin mRNAs during long-term cetuximab treatment of KRAS wild-type tumor cells.Invest New Drugs. 2012 Apr;30(2):846-52. doi: 10.1007/s10637-010-9612-2. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Invest New Drugs. 2012. PMID: 21161326
-
Clinical and economic value of screening for Kras mutations as predictors of response to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2009 Dec 1;66(23):2105-12. doi: 10.2146/ajhp090036. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2009. PMID: 19923311 Review.
-
Molecular predictors of efficacy to anti-EGFR agents in colorectal cancer patients.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2010 Feb;10(1):68-79. doi: 10.2174/156800910790980205. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20088793 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Receptor Targeted Fluorescent Imaging for Gallbladder Cancer in Orthotopic Mouse Models.Gut Liver. 2022 Jul 15;16(4):606-612. doi: 10.5009/gnl210164. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Gut Liver. 2022. PMID: 34462395 Free PMC article.
-
The anticancer effect of EGFR-targeting artificial microRNA controlled by SLPI promoter in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Nov;36(11):e24729. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24729. Epub 2022 Oct 25. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 36284372 Free PMC article.
-
L1 Cell Adhesion Molecule Promotes Migration and Invasion via JNK Activation in Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Cells with Activating KRAS Mutation.Mol Cells. 2017 May 31;40(5):363-370. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2017.2282. Epub 2017 May 24. Mol Cells. 2017. PMID: 28535665 Free PMC article.
-
The irreversible pan-HER inhibitor PF00299804 alone or combined with gemcitabine has an antitumor effect in biliary tract cancer cell lines.Invest New Drugs. 2012 Dec;30(6):2148-60. doi: 10.1007/s10637-011-9782-6. Epub 2011 Dec 25. Invest New Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22197904
-
Expression and activation of EGFR and STAT3 during the multistage carcinogenesis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma induced by 3'-methyl-4 dimethylaminoazobenzene in rats.J Toxicol Pathol. 2015 Apr;28(2):79-87. doi: 10.1293/tox.2014-0047. Epub 2015 Feb 9. J Toxicol Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26028817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mittal B, Deutsch M, Iwatsuki S. Primary cancers of extrahepatic biliary passages. International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics. 1985;11(4):849–854. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

