Mutations in TGFbeta-RII and BAX mediate tumor progression in the later stages of colorectal cancer with microsatellite instability
- PMID: 20565851
- PMCID: PMC2927997
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-303
Mutations in TGFbeta-RII and BAX mediate tumor progression in the later stages of colorectal cancer with microsatellite instability
Abstract
Background: Microsatellite instability (MSI) occurs in 15% of colorectal cancers (CRC). The genetic targets for mutation in the MSI phenotype include somatic mutations in the transforming growth factor beta receptor typeII (TGFbetaRII), BAX, hMSH3 and hMSH6. It is not clear how mutations of these genes mediate tumor progression in the MSI pathway, and the temporal sequence of these mutations remains uncertain. In this study, early stage CRCs were examined for frameshift mutations in these target genes, and compared with late stage tumors and CRC cell lines.
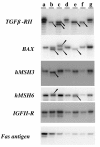
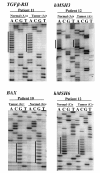
Methods: We investigated 6 CRC cell lines and 71 sporadic CRCs, including 61 early stage cancers and 10 late stage cancers. Mutations of repetitive mononucleotide tracts in the coding regions of TGFbetaRII, BAX, hMSH3, hMSH6, IGFIIR and Fas antigen were identified by direct sequencing.
Results: Thirteen (18.3%) of 71 CRC, including 9/61 (14.7%) early stage cancers and 4/10 (40%) late stage cancers, were identified as MSI and analyzed for frameshift mutations. No mutation in the target genes was observed in any of the 9 early stage MSI CRCs. In contrast, frameshift mutations of TGFbetaRII, BAX, hMSH3 and hMSH6 were present in 3/4 late stage MSI tumors. There is a statistical association (p = 0.014) between mutation in any one gene and tumor stage.
Conclusions: TGFbetaRII, BAX, hMSH3 and hMSH6 mutations are relatively late events in the genesis of MSI CRCs. The frameshift mutations in these target genes might mediate progression from early to late stage cancer, rather than mediating the adenoma to carcinoma transition.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[The relationship between frameshift mutations of transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor, insulin growth factor II receptor, bcl-2 associated X protein, E2F4 and microsatellite instability in gastric carcinoma].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2006 Mar 1;44(5):344-8. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16635398 Chinese.
-
Genetic progression in microsatellite instability high (MSI-H) colon cancers correlates with clinico-pathological parameters: A study of the TGRbetaRII, BAX, hMSH3, hMSH6, IGFIIR and BLM genes.Int J Cancer. 2000 May 20;89(3):230-5. Int J Cancer. 2000. PMID: 10861498
-
Mutations in hMSH6 alone are not sufficient to cause the microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer cell lines.Eur J Cancer. 1999 Nov;35(12):1724-9. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(99)00206-3. Eur J Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10674020
-
The clinicopathological features of gastric carcinomas with microsatellite instability may be mediated by mutations of different "target genes": a study of the TGFbeta RII, IGFII R, and BAX genes.Am J Pathol. 1998 Oct;153(4):1211-9. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)65665-9. Am J Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9777952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and progression of colorectal neoplasia.Cancer Biomark. 2010;9(1-6):235-65. doi: 10.3233/CBM-2011-0160. Cancer Biomark. 2010. PMID: 22112479 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lymphoma-like T cell infiltration in liver is associated with increased copy number of dominant negative form of TGFβ receptor II.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49413. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049413. Epub 2012 Nov 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23145171 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular-targeted therapy toward precision medicine for gastrointestinal caner: Current progress and challenges.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021 May 15;13(5):366-390. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i5.366. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34040699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutational Profiles Reveal an Aberrant TGF-β-CEA Regulated Pathway in Colon Adenomas.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 21;11(4):e0153933. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153933. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27100181 Free PMC article.
-
B4GALT1-dependent galectin-8 binding with TGF-β receptor suppresses colorectal cancer progression and metastasis.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Sep 4;15(9):654. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07028-3. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39231945 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β Signaling in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (mCRC): From Underlying Mechanism to Potential Applications in Clinical Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 20;23(22):14436. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214436. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430910 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pedroni M, Sala E, Scarselli A, Borghi F, Menigatti M, Benatti P, Percesepe A, Rossi G, Foroni M, Losi L. et al.Microsatellite instability and mismatch-repair protein expression in hereditary and sporadic colorectal carcinogenesis. Cancer research. 2001;61(3):896–899. - PubMed
-
- Kambara T, Matsubara N, Nakagawa H, Notohara K, Nagasaka T, Yoshino T, Isozaki H, Sharp GB, Shimizu K, Jass J. et al.High frequency of low-level microsatellite instability in early colorectal cancer. Cancer research. 2001;61(21):7743–7746. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

