Dietary red palm oil supplementation reduces myocardial infarct size in an isolated perfused rat heart model
- PMID: 20565865
- PMCID: PMC2906443
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-64
Dietary red palm oil supplementation reduces myocardial infarct size in an isolated perfused rat heart model
Abstract
Background and aims: Recent studies have shown that dietary red palm oil (RPO) supplementation improves functional recovery following ischaemia/reperfusion in isolated hearts. The main aim of this study was to investigate the effects of dietary RPO supplementation on myocardial infarct size after ischaemia/reperfusion injury. The effects of dietary RPO supplementation on matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP2) activation and PKB/Akt phosphorylation were also investigated.
Materials and methods: Male Wistar rats were divided into three groups and fed a standard rat chow diet (SRC), a SRC supplemented with RPO, or a SRC supplemented with sunflower oil (SFO), for a five week period, respectively. After the feeding period, hearts were excised and perfused on a Langendorff perfusion apparatus. Hearts were subjected to thirty minutes of normothermic global ischaemia and two hours of reperfusion. Infarct size was determined by triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining. Coronary effluent was collected for the first ten minutes of reperfusion in order to measure MMP2 activity by gelatin zymography.
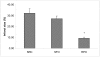
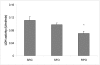
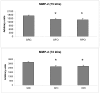
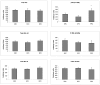
Results: Dietary RPO-supplementation decreased myocardial infarct size significantly when compared to the SRC-group and the SFO-supplemented group (9.1 +/- 1.0% versus 30.2 +/- 3.9% and 27.1 +/- 2.4% respectively). Both dietary RPO- and SFO-supplementation were able to decrease MMP2 activity when compared to the SRC fed group. PKB/Akt phosphorylation (Thr 308) was found to be significantly higher in the dietary RPO supplemented group when compared to the SFO supplemented group at 10 minutes into reperfusion. There was, however, no significant changes observed in ERK phosphorylation.
Conclusions: Dietary RPO-supplementation was found to be more effective than SFO-supplementation in reducing myocardial infarct size after ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Both dietary RPO and SFO were able to reduce MMP2 activity, which suggests that MMP2 activity does not play a major role in protection offered by RPO. PKB/Akt phosphorylation may, however, be involved in RPO mediated protection.
Figures

References
-
- Bester DJ, Van Rooyen J, Du Toit EF, Esterhuyse AJ. Red palm oil protects against the consequences of oxidative stress when supplemented with dislipidaemic diets. Medical Technology SA. 2006;20(1):3–10.
-
- Esterhuyse AJ, Du Toit EF, Benade AJS, Van Rooyen J. Dietary red palm oil improves reperfusion cardiac function in the isolated perfused rat heart of animals fed a high cholesterol diet. PLEFA. 2005;72:153–161. - PubMed
-
- Esterhuyse JS, Van Rooyen J, Strijdom H, Bester D, Du Toit EF. Proposed mechanisms for red palm oil induced cardioprotection in a model of hyperlipidaemia in the rat. PLEFA. 2006;75:375–384. - PubMed
-
- Van Rooyen J, Esterhuyse AJ, Engelbrecht AM, Du Toit EF. Health benefits of a natural carotenoid rich oil: a proposed mechanism of protection against ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2008;17(Suppl 1):316–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

