Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ signalling is involved in estradiol-induced breast cancer epithelial cell growth
- PMID: 20565939
- PMCID: PMC2906470
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-156
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ signalling is involved in estradiol-induced breast cancer epithelial cell growth
Abstract
Background: Ca2+ is a ubiquitous messenger that has been shown to be responsible for controlling numerous cellular processes including cell growth and cell death. Whereas the involvement of IP3-induced Ca2+ signalling (IICS) in the physiological activity of numerous cell types is well documented, the role of IICS in cancer cells is still largely unknown. Our purpose was to characterize the role of IICS in the control of growth of the estrogen-dependent human breast cancer epithelial cell line MCF-7 and its potential regulation by 17beta-estradiol (E2).
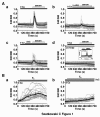
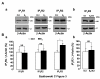
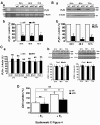
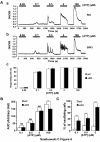
Results: Our results show that the IP3 receptor (IP3R) inhibitors caffeine, 2-APB and xestospongin C (XeC) inhibited the growth of MCF-7 stimulated by 5% foetal calf serum or 10 nM E2. Furthermore, Ca2+ imaging experiments showed that serum and E2 were able to trigger, in a Ca2+-free medium, an elevation of internal Ca2+ in a 2-APB and XeC-sensitive manner. Moreover, the phospholipase C (PLC) inhibitor U-73122 was able to prevent intracellular Ca2+ elevation in response to serum, whereas the inactive analogue U-73343 was ineffective. Western-blotting experiments revealed that the 3 types of IP3Rs are expressed in MCF-7 cells and that a 48 hours treatment with 10 nM E2 elevated IP3R3 protein expression level in an ICI-182,780 (a specific estrogen receptor antagonist)-dependent manner. Furthermore, IP3R3 silencing by the use of specific small interfering RNA was responsible for a drastic modification of the temporal feature of IICS, independently of a modification of the sensitivity of the Ca2+ release process and acted to counteract the proliferative effect of 10 nM E2.
Conclusions: Altogether, our results are in favour of a role of IICS in MCF-7 cell growth, and we hypothesize that the regulation of IP3R3 expression by E2 is involved in this effect.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular interaction and functional coupling between type 3 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor and BKCa channel stimulate breast cancer cell proliferation.Eur J Cancer. 2013 Nov;49(17):3738-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.07.013. Epub 2013 Aug 27. Eur J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23992640
-
Possible involvement of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 3 (IP3R3) in the peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancers.Anticancer Res. 2003 Sep-Oct;23(5A):3691-7. Anticancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14666665
-
Dynamic clustering of IP3 receptors by IP3.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Apr;40(2):325-30. doi: 10.1042/BST20110772. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 22435806 Review.
-
Stable expression of truncated inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor subunits in 3T3 fibroblasts. Coordinate signaling changes and differential suppression of cell growth and transformation.J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 29;269(30):19216-24. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 8034682
-
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-isoform diversity in cell death and survival.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Oct;1843(10):2164-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.03.007. Epub 2014 Mar 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24642269 Review.
Cited by
-
Type 3 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor has antiapoptotic and proliferative role in cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Feb 22;10(3):186. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1433-4. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30796197 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Dimorphism in a Reciprocal Interaction of Ryanodine and IP3 Receptors in the Induction of Hyperalgesic Priming.J Neurosci. 2017 Feb 22;37(8):2032-2044. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2911-16.2017. Epub 2017 Jan 23. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28115480 Free PMC article.
-
IP3 Receptor-Mediated Calcium Signaling and Its Role in Autophagy in Cancer.Front Oncol. 2017 Jul 5;7:140. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00140. eCollection 2017. Front Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28725634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potentially functional variants of HBEGF and ITPR3 in GnRH signaling pathway genes predict survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients.Transl Res. 2021 Jul;233:92-103. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2020.12.009. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 33400994 Free PMC article.
-
Type 3 IP3 receptor: Its structure, functions, and related disease implications.Channels (Austin). 2023 Dec;17(1):2267416. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2023.2267416. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Channels (Austin). 2023. PMID: 37818548 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vucenik I, Ramakrishna G, Tantivejkul K, Anderson LM, Ramljak D. Inositol hexaphosphate (IP6) blocks proliferation of human breast cancer cells through a PKCδ-dependent increase in p27Kip1 and decrease in retinoblastoma protein (pRb) phosphorylation. Breast Cancer Res and Tr. 2005;91:35–45. doi: 10.1007/s10549-004-6456-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

