Can satellite glial cells be therapeutic targets for pain control?
- PMID: 20566001
- PMCID: PMC3139431
- DOI: 10.1017/S1740925X10000098
Can satellite glial cells be therapeutic targets for pain control?
Abstract
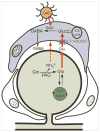
Satellite glial cells (SGCs) undergo phenotypic changes and divide the following injury into a peripheral nerve. Nerve injury, also elicits an immune response and several antigen-presenting cells are found in close proximity to SGCs. Silencing SCG-specific molecules involved in intercellular transport (Connexin 43) or glutamate recycling (glutamine synthase) can dramatically alter nociceptive responses of normal and nerve-injured rats. Transducing SGCs with glutamic acid decarboxylase can produce analgesia in models of trigeminal pain. Taken together these data suggest that SGCs may play a role in the genesis or maintenance of pain and open a range of new possibilities for curing neuropathic pain.
Figures




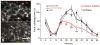
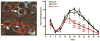
References
-
- Adler JE, Nico L, VandeVord P, Skoff AM. Modulation of neuropathic pain by a glial-derived factor. Pain Medicine. 2009;10:1229–1236. - PubMed
-
- Bhargava A, Dallman MF, Pearce D, Choi S. Long double-stranded RNA-mediated RNA interference as a tool to achieve site-specific silencing of hypothalamic neuropeptides. Brain Research and Brain Research Protocol. 2004;13:115–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

